Radon and Lung Cancer: Current Trends and Future Perspectives
- PMID: 35804914
- PMCID: PMC9264880
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14133142
Radon and Lung Cancer: Current Trends and Future Perspectives
Abstract
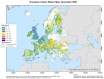
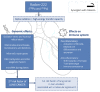
Lung cancer is a public health problem and the first cause of cancer death worldwide. Radon is a radioactive gas that tends to accumulate inside homes, and it is the second lung cancer risk factor after smoking, and the first one in non-smokers. In Europe, there are several radon-prone areas, and although the 2013/59 EURATOM directive is aimed to regulate indoor radon exposition, regulating measures can vary between countries. Radon emits alpha-ionizing radiation that has been linked to a wide variety of cytotoxic and genotoxic effects; however, the link between lung cancer and radon from the genomic point of view remains poorly described. Driver molecular alterations have been recently identified in non-small lung cancer (NSCLC), such as somatic mutations (EGFR, BRAF, HER2, MET) or chromosomal rearrangements (ALK, ROS1, RET, NTRK), mainly in the non-smoking population, where no risk factor has been identified yet. An association between radon exposure and oncogenic NSCLC in non-smokers has been hypothesised. This paper provides a practical, concise and updated review on the implications of indoor radon in lung cancer carcinogenesis, and especially of its potential relation with NSCLC with driver genomic alterations.
Keywords: carcinogenesis; driver genomic alterations; lung cancer; non-smokers; radon.
Conflict of interest statement
M.R.: No conflicts of interest; M.G.d.H.: No conflicts of interest; L.M.: reports receiving research grant/funding (self) from Bristol–Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Amgen, Stilla and Inivata; serving in advisory/consultancy for Roche, Takeda and Jannsen; receiving honoraria (self) from Bristol–Myers Squibb, Takeda and Roche; receiving travel/accommodation/expenses from Roche, Bristol–Myers Squibb, Takeda and AstraZeneca; B.B.: Sponsored Research at Gustave Roussy Cancer Center Abbvie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Biogen, Blueprint Medicines, BMS, Celgene, Eli Lilly, GSK, Ignyta, IPSEN, Merck KGaA, MSD, Nektar, Onxeo, Pfizer, Pharma Mar, Sanofi, Spectrum Pharmaceuticals, Takeda and Tiziana Pharma.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Indoor Radon in EGFR- and BRAF-Mutated and ALK-Rearranged Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients.Clin Lung Cancer. 2019 Jul;20(4):305-312.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2019.04.009. Epub 2019 May 3. Clin Lung Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31151782
-
[Driver genes expression and clinical characteristics of targeted therapy in non-small cell lung cancer in Yunnan-Kweichow Plateau].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2020 Sep 23;42(9):735-740. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112152-20200323-00248. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32988155 Chinese.
-
Indoor radon exposure and lung cancer: a review of ecological studies.Ann Occup Environ Med. 2016 Mar 25;28:15. doi: 10.1186/s40557-016-0098-z. eCollection 2016. Ann Occup Environ Med. 2016. PMID: 27019716 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitors for patients with advanced lung cancer and oncogenic driver alterations: results from the IMMUNOTARGET registry.Ann Oncol. 2019 Aug 1;30(8):1321-1328. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdz167. Ann Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31125062 Free PMC article.
-
An updated review of case-control studies of lung cancer and indoor radon-Is indoor radon the risk factor for lung cancer?Ann Occup Environ Med. 2016 Mar 3;28:9. doi: 10.1186/s40557-016-0094-3. eCollection 2016. Ann Occup Environ Med. 2016. PMID: 26949535 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
High-Throughput Computational Screening of Two-Dimensional Covalent Organic Frameworks (2D COFs) for Capturing Radon in Moist Air.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 May 3;13(9):1532. doi: 10.3390/nano13091532. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37177077 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial Dynamics in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Aug 12;16(16):2823. doi: 10.3390/cancers16162823. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39199596 Free PMC article.
-
Radon Exposure in the Underground Tourist Route-Historic Silver Mine in Tarnowskie Góry, Poland.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Nov 27;19(23):15778. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192315778. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36497854 Free PMC article.
-
Opportunities and Challenges of Kava in Lung Cancer Prevention.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 31;24(11):9539. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119539. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radon Exposure and Cancer Risk: Assessing Genetic and Protein Markers in Affected Populations.Biology (Basel). 2025 May 6;14(5):506. doi: 10.3390/biology14050506. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40427695 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alberg A.J., Brock M.V., Ford J.G., Samet J.M., Spivack S.D. Epidemiology of Lung Cancer: Diagnosis and Management of Lung Cancer, 3rd Ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest. 2013;143((Suppl. S5)):e1S–e29S. doi: 10.1378/chest.12-2345. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Office of the Surgeon General (US) Office on Smoking and Health (US) The Health Consequences of Smoking: A Report of the Surgeon General. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (US); Atlanta, GA, USA: 2004. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

