The Role of the Immune System in the Development of Endometriosis
- PMID: 35805112
- PMCID: PMC9265783
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11132028
The Role of the Immune System in the Development of Endometriosis
Abstract
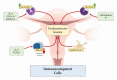
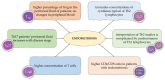
Endometriosis is a chronic disease that affects about 10% of women of reproductive age. It can contribute to pelvic pain, infertility or other conditions such as asthma, cardiovascular disease, breast or ovarian cancer. Research has shown that one of the conditions for the development of endometrial lesions is the dysfunction of the immune system. It appears that immune cells, such as neutrophils, macrophages, NK cells and dendritic cells, may play a specific role in the angiogenesis, growth and invasion of endometriosis cells. Immune cells secrete cytokines and defensins that also affect the endometriosis environment. This review discusses the various components of the immune system that are involved in the formation of endometrial lesions in women.
Keywords: cytokine; defensins; endometriosis; immune system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Smycz-Kubańska M., Kondera-Anasz Z., Sikora J., Wendlocha D., Królewska-Daszczyńska P., Englisz A., Janusz A., Janusz J., Mielczarek-Palacz A. The Role of Selected Chemokines in the Peritoneal Fluid of Women with Endometriosis—Participation in the Pathogenesis of the Disease. Processes. 2021;9:2229. doi: 10.3390/pr9122229. - DOI
-
- Sampson J.A. Peritoneal Endometriosis Due to the Menstrual Dissemination of Endometrial Tissue into the Peritoneal Cavity. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1927;14:422–469. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9378(15)30003-X. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical