An In-Depth Examination of the Natural Radiation and Radioactive Dangers Associated with Regularly Used Medicinal Herbs
- PMID: 35805783
- PMCID: PMC9266100
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19138124
An In-Depth Examination of the Natural Radiation and Radioactive Dangers Associated with Regularly Used Medicinal Herbs
Abstract
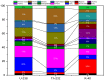
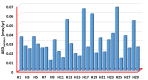
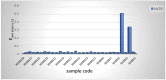
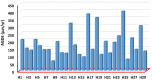
The specific activity of U-238 and Th-232, as well as K-40 radionuclides, in twenty-nine investigated medicinal herbs used in Egypt has been measured using a high-purity germanium (HP Ge) detector. The measured values ranged from the BDL to 20.71 ± 1.52 with a mean of 7.25 ± 0.54 (Bq kg-1) for uranium-238, from the BDL to 29.35 ± 1.33 with a mean of 7.78 ± 0.633 (Bq kg-1) for thorium-232, and from 172 ± 5.85 to 1181.2 ± 25.5 with a mean of 471.4 ± 11.33 (Bq kg-1) for potassium-40. Individual herbs with the highest activity levels were found to be 20.71 ± 1.52 (Bq kg-1) for uranium-238 (H4, Thyme herb), 29.35 ± 1.33 (Bq kg-1) for thorium-232 (H20, Cinnamon), and 1181.2 ± 25.5 (Bq kg-1) for potassium-40 (H24, Worm-wood). (AACED) Ingestion-related effective doses over the course of a year of uranium-238 and thorium-232, as well as potassium-40 estimated from measured activity concentrations, are 0.002304 ± 0.00009 (minimum), 0.50869 ± 0.0002 (maximum), and 0.0373 ± 0.0004 (average)(mSv/yr). Radium equivalent activity (Raeq), annual gonadal dose equivalent (AGDE), absorbed gamma dose rate (Doutdoor, Dindoor), gamma representative level index (I), annual effective dose (AEDtotal), external and internal hazard index (Hex, Hin), and excess lifetime cancer risk were determined in medicinal plants (ELCR). The radiological hazards assessment revealed that the investigated plant species have natural radioactivity levels that are well within the internationally recommended limit. This is the first time that the natural radioactivity of therapeutic plants has been measured in Egypt. In addition, no artificial radionuclide (for example, 137Cs) was discovered in any of the samples. Therefore, the current findings are intended to serve as the foundation for establishing a standard safety and guideline for using these therapeutic plants in Egypt.
Keywords: high-purity germanium; medical herb; natural radiation; radioactive risks.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Harb S.M. Natural radioactivity concentrations in some medicinal plants and annual committed effective dose from their consumption. Radiat. Prot. Environ. 2015;38:35. doi: 10.4103/0972-0464.162816. - DOI
-
- Kessaratikoon P., Boonkrongcheep R., Polthum S. Measurement of radionuclides in surface soil and beach sand samples from Rayong Province (Thailand) and the evaluation of excess lifetime cancer risk. ScienceAsia. 2021;47:120–129. doi: 10.2306/scienceasia1513-1874.2021.S016. - DOI
-
- Sharmila S., Kalaichelvi K. Anatomical Characterization on the Leaf of Cayratia pedata var. glabra (Lam.) Gagnep. var. glabra Gamble (Vitaceae)—An Endemic Climber of Western Ghats, India. ScieXplore Int. J. Res. Sci. 2016;3:21. doi: 10.15613/sijrs/2016/v3i1/136477. - DOI
-
- World Health Organization . WHO Guidelines for Assessing Quality of Herbal Medicines with Reference to Contaminants and Residues. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2007.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

