Bone Tissue Engineering in Rat Calvarial Defects Using Induced Bone-like Tissue by rhBMPs from Immature Muscular Tissues In Vitro
- PMID: 35805943
- PMCID: PMC9266849
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23136927
Bone Tissue Engineering in Rat Calvarial Defects Using Induced Bone-like Tissue by rhBMPs from Immature Muscular Tissues In Vitro
Abstract
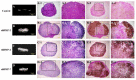
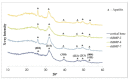
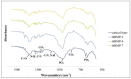
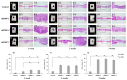
This study aimed to induce bone-like tissue from immature muscular tissue (IMT) in vitro using commercially available recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein (rhBMP)-2, rhBMP-4, and rhBMP-7, and then implanting this tissue into a calvarial defect in rats to assess healing. IMTs were extracted from 20-day-old Sprague-Dawley (SD) fetal rats, placed on expanded polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE) with 10 ng/μL each of rhBMP-2, BMP-4, and BMP-7, and cultured for two weeks. The specimens were implanted into calvarial defects in 3-week-old SD rats for up to three weeks. Relatively strong radiopacity was observed on micro-CT two weeks after culture, and bone-like tissue, comprising osteoblastic cells and osteoids, was partially observed by H&E staining. Calcium, phosphorus, and oxygen were detected in the extracellular matrix using an electron probe micro analyzer, and X-ray diffraction patterns and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy spectra of the specimen were found to have typical apatite crystal peaks and spectra, respectively. Furthermore, partial strong radiopacity and ossification were confirmed one week after implantation, and a dominant novel bone was observed after two weeks in the defect site. Thus, rhBMP-2, BMP-4, and BMP-7 differentiated IMT into bone-like tissue in vitro, and this induced bone-like tissue has ossification potential and promotes the healing of calvarial defects. Our results suggest that IMT is an effective tissue source for bone tissue engineering.
Keywords: bone tissue engineering; expanded polytetrafluoroethylene; immature muscular tissue; induced bone-like tissue; recombinant human bone morphogenetic proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

