Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes and Intervertebral Disc Regeneration: Review
- PMID: 35806304
- PMCID: PMC9267028
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23137306
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes and Intervertebral Disc Regeneration: Review
Abstract
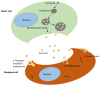
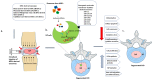
Intervertebral disc degeneration (IVDD) is a common cause of lower back pain (LBP), which burdens individuals and society as a whole. IVDD occurs as a result of aging, mechanical trauma, lifestyle factors, and certain genetic abnormalities, leads to loss of nucleus pulposus, alteration in the composition of the extracellular matrix, excessive oxidative stress, and inflammation in the intervertebral disc. Pharmacological and surgical interventions are considered a boon for the treatment of IVDD, but the effectiveness of those strategies is limited. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have recently emerged as a possible promising regenerative therapy for IVDD due to their paracrine effect, restoration of the degenerated cells, and capacity for differentiation into disc cells. Recent investigations have shown that the pleiotropic effect of MSCs is not related to differentiation capacity but is mediated by the secretion of soluble paracrine factors. Early studies have demonstrated that MSC-derived exosomes have therapeutic potential for treating IVDD by promoting cell proliferation, tissue regeneration, modulation of the inflammatory response, and reduced apoptosis. This paper highlights the current state of MSC-derived exosomes in the field of treatment of IVDD with further possible future developments, applications, and challenges.
Keywords: exosomes; intervertebral disc degeneration; lower back pain; mesenchymal stem cell; regeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

