Effect of Silver Diamine Fluoride and Potassium Iodide Solution on Enamel Remineralization and Discoloration in Artificial Caries
- PMID: 35806648
- PMCID: PMC9267504
- DOI: 10.3390/ma15134523
Effect of Silver Diamine Fluoride and Potassium Iodide Solution on Enamel Remineralization and Discoloration in Artificial Caries
Abstract
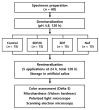
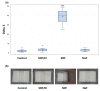
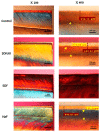
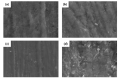
Silver diamine fluoride (SDF) is a strong fluoride agent for caries control, remineralization, and reducing the incidence of dental caries. This study used 38% SDF with potassium iodide (KI) on enamel remineralization and compared it with the currently used 38% SDF and 5% sodium fluoride (NaF) varnish to treat artificial caries. Bovine incisors were demineralized for 120 h and randomly distributed for treatment by the remineralization agents for 120 h as follows: control (n = 15), SDF/KI (n = 15), SDF (n = 15), and NaF (n = 15). Colorimetric analysis was performed using the ΔE value. The Vickers microhardness (VHN) was determined to evaluate the enamel remineralization of the specimens. Polarized light microscopy (PLM) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) were performed to confirm the surfaces precisely and histologically. SDF/KI caused no significant difference in discoloration between the control and NaF groups. There was also no significant difference in the VHN after remineralization, but SDF/KI exhibited the highest mean microhardness. PLM revealed that SDF/KI had the greatest remineralization ability. In conclusion, SDF/KI is effective for dental enamel remineralization even with KI, which reduces discoloration.
Keywords: NaF varnish; discoloration; enamel remineralization; potassium iodide; silver diamine fluoride.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

