Investigation of MAO Coatings Characteristics on Titanium Products Obtained by EBM Method Using Additive Manufacturing
- PMID: 35806660
- PMCID: PMC9267494
- DOI: 10.3390/ma15134535
Investigation of MAO Coatings Characteristics on Titanium Products Obtained by EBM Method Using Additive Manufacturing
Abstract
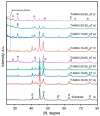
Coatings with a thickness from 27 to 62 µm on electron beam melted Ti-6Al-4V have been formed by micro-arc oxidation (MAO) in a silicate-hypophosphite electrolyte. MAO tests in the anode-cathode mode (50 Hz) with an anode-to-cathode current ratio of 1:1 and sum current densities 10 and 20 A/dm2 were carried out. The duration of the MAO treatment was 30 and 60 min. The effect of the processing parameters on the structural properties of the MAO treated coatings was studied. The current density and treatment time significantly affect the coating thickness and surface roughness. The values of these characteristics increase as the current density increases. The effect of thermal cycling tests on surface morphology, thickness and roughness, and elemental and phase composition of MAO coatings was analyzed. After 50 cycles of thermal cycling from +200 °C to -50 °C, no cracking or delamination of coatings was observed. Coatings formed in 30 min at a current density of 20 A/dm2 turned out to be the best in terms of such indicators as surface morphology, thickness, and roughness.
Keywords: MAO coating; additive manufacturing; composition; electron beam melting; heat resistance; micro-arc oxidation; roughness; structure; surface morphology; thermal cycling test; thickness; titanium alloy Ti-6Al-4V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Prasad S., Ehrensberger M., Gibson M.P., Kim H., Monaco E.A., Jr. Biomaterial properties of titanium dentistry. J. Oral Biosci. 2015;57:192–199. doi: 10.1016/j.job.2015.08.001. - DOI
-
- Buj-Corral I., Tejo-Otero A., Fenollosa-Artes F. Development of AM Technologies for Metals in the Sector of Medical Implants. Metals. 2020;10:686. doi: 10.3390/met10050686. - DOI
-
- Ferraris S., Spriano S. Porous Titanium by Additive Manufacturing: A Focus on Surfaces for Bone Integration. Metals. 2021;11:1343. doi: 10.3390/met11091343. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

