Preexisting Humoral Immunity Cross-Reacting with SARS-CoV-2 Might Prevent Death Due to COVID-19 in Critical Patients
- PMID: 35807155
- PMCID: PMC9267280
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11133870
Preexisting Humoral Immunity Cross-Reacting with SARS-CoV-2 Might Prevent Death Due to COVID-19 in Critical Patients
Abstract
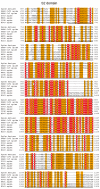
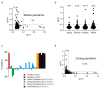
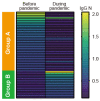
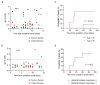
The preexistence of humoral immunity, which cross-reacts with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) protein due to prior endemic low-pathogenic human coronavirus infection, has been reported, but its role in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outcomes remains elusive. We evaluated serum samples obtained from 368 patients before the pandemic and 1423 independent serum samples from patients during the pandemic. We found that approximately 6~13% and 1.5% of patients had IgG cross-reactivity to the SARS-CoV-2 spike and nucleocapsid proteins in both cohorts. We evaluated the IgG cross-reactivity to the SARS-CoV-2 spike and nucleocapsid proteins in 48 severe or critical COVID-19 patients to evaluate if the elevation of IgG was evoked as a primary response (IgG elevation from 10 days after antigen exposure) or boosted as a secondary response (IgG elevation immediately after antigen exposure). Approximately 50% of patients showed humoral immune responses to the nucleocapsid protein of SARS-CoV-2. Importantly, none of the critically ill patients with this humoral immunity died, whereas 40% of patients without this immunity did. Taken together, subjects had humoral immunity to SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid but not spike before the pandemic, which might prevent critically ill COVID-19 patients from dying.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; humoral immune memory; mortality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Shrwani K., Sharma R., Krishnan M., Jones T., Mayora-Neto M., Cantoni D., Temperton N.J., Dobson S.L., Subramaniam K., McNamara P.S., et al. Detection of Serum Cross-Reactive Antibodies and Memory Response to SARS-CoV-2 in Prepandemic and Post-COVID-19 Convalescent Samples. J. Infect. Dis. 2021;224:1305–1315. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiab333. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anderson E.M., Goodwin E.C., Verma A., Arevalo C.P., Bolton M.J., Weirick M.E., Gouma S., McAllister C.M., Christensen S.R., Weaver J., et al. Seasonal human coronavirus antibodies are boosted upon SARS-CoV-2 infection but not associated with protection. Cell. 2021;184:1858–1864.e1810. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.02.010. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cubuk J., Alston J.J., Incicco J.J., Singh S., Stuchell-Brereton M.D., Ward M.D., Zimmerman M.I., Vithani N., Griffith D., Wagoner J.A., et al. The SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein is dynamic, disordered, and phase separates with RNA. Nat. Commun. 2021;12:1936. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21953-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

