Foliar Application of Salicylic Acid to Mitigate Water Stress in Tomato
- PMID: 35807727
- PMCID: PMC9268784
- DOI: 10.3390/plants11131775
Foliar Application of Salicylic Acid to Mitigate Water Stress in Tomato
Abstract
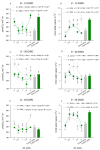
Salicylic acid (SA) is an important plant regulator reported as a mitigator of water deficit in plants, however without a recommendation for use in field conditions. Thus, this research aims to validate the use of SA under field conditions in regions with low water availability. For that, we evaluated CO2 assimilation (A), stomatal conductance (gs), transpiration (E), water use efficiency (WUE), and carboxylation efficiency (A/Ci) at 15, 30, and 45 days of continuous stress water deficit, as well as the application of salicylic acid (0.0; 0.5; 1.0; 1.5; 2.0 mM) in tomato plants subjected to continuous water deficit (45 days), in two years (2019 and 2020). The water deficit reduced the A, gs, E and A/Ci, while the foliar application of SA increased these parameters in all evaluated times, resulting in similar or even higher values than in plants without water deficit. Water deficit caused floral abortion in tomato plants, without the application of SA, reducing the number of fruit production. In contrast, plants that received about 1.3 mM of SA increased A and A/Ci and translocated the photo-assimilates, mainly to flowers and fruits, reducing floral abortion and increasing fruit production. Thus, foliar application of SA was efficient in mitigating the deleterious effects of water deficit in tomato plants regarding the gas exchange and fruit production.
Keywords: Solanum lycopersicum; floral abortion; photosynthesis; plant regulation; water deficit.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Gomes A.M.F., Nhantumbo N., Ferreira-Pinto M., Massinga R., Ramalho J.C., Ribeiro-Barros A. Legume Crops—Characterization and Breeding for Improved Food Security. IntechOpen; London, UK: 2019. Breeding Elite Cowpea [Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp] Varieties for Improved Food Security and Income in Africa: Opportunities and Challenges; pp. 626–640. - DOI
-
- Hasanuzzaman M., Fugita M., Oku H., Islam M.T. Plant Tolerance to Environmental Stress: Role of Phytoprotectants. 1st ed. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2019. p. 488.
-
- Ullah H., Luc P.D., Gautam A., Datta A. Growth, Yield and Silicon Uptake of Rice (Oryza sativa) As Influenced by Dose and Timing of Silicon Application under Water-Deficit Stress. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2018;64:318–330. doi: 10.1080/03650340.2017.1350782. - DOI
-
- Sirisuntornlak N., Ghafoori S., Datta A., Arirob W. Seed Priming and Soil Incorporation with Silicon Influence Growth and Yield of Maize under Water-Deficit Stress. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2019;65:197–207. doi: 10.1080/03650340.2018.1492713. - DOI
-
- Chakma R., Biswas A., Saekong P., Ullah H., Datta A. Foliar Application and Seed Priming of Salicylic Acid Affect Growth, Fruit Yield, and Quality of Grape Tomato under Drought Stress. Sci. Hortic. 2021;280:109904. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2021.109904. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

