Clinical Correlates of Measured and Predicted Resting Energy Expenditure in Patients with Anorexia Nervosa: A Retrospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 35807906
- PMCID: PMC9269154
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14132727
Clinical Correlates of Measured and Predicted Resting Energy Expenditure in Patients with Anorexia Nervosa: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
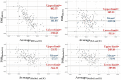
Resting energy expenditure (REE; i.e., the calorie amount required for 24 h during a non-active period) is an important parameter in nutritional rehabilitation of patients with anorexia nervosa (AN). This study determined whether age, body mass index, AN duration/subtype/specific symptoms/clinical severity, cognitive function alterations, and psychiatric comorbidities influenced REE or the difference between the calculated and estimated REE. Patients with AN who were followed at a daycare treatment facility between May 2017 and January 2020 (n = 138) underwent a complete assessment that included the MINI, Eating Disorder Examination Questionnaire, d2 test of attention, body fat composition by bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) and REE measurement by indirect calorimetry (REEIC). AN subtype (N = 66 for restrictive subtype and N = 69 for non-restrictive subtype; p = 0.005), free-fat mass (<0.001), and fat mass (<0.001) were associated with REEIC. Age (p < 0.001), height (p = 0.003), and AN duration (N = 46 for <3 years and N = 82 for ≥3 years; p = 0.012) were associated with the difference between estimated REE (using the Schebendach equation) and measured REEIC. Therefore, the Schebendach equation was adjusted differently in the two patients’ subgroups (AN duration ≤ or >3 years). Overall, REE was higher in patients with restrictive than non-restrictive AN. In the absence of BIA measures, REE-estimating equations should take into account AN duration.
Keywords: AN duration; AN subtype; anorexia nervosa; resting energy expenditure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

