Self-Assembled Nanoscale Materials for Neuronal Regeneration: A Focus on BDNF Protein and Nucleic Acid Biotherapeutic Delivery
- PMID: 35808102
- PMCID: PMC9268293
- DOI: 10.3390/nano12132267
Self-Assembled Nanoscale Materials for Neuronal Regeneration: A Focus on BDNF Protein and Nucleic Acid Biotherapeutic Delivery
Abstract
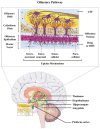
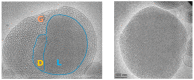
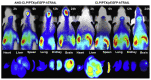
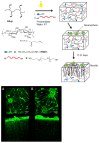
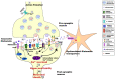
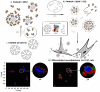
Enabling challenging applications of nanomedicine and precision medicine in the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders requires deeper investigations of nanocarrier-mediated biomolecular delivery for neuronal targeting and recovery. The successful use of macromolecular biotherapeutics (recombinant growth factors, antibodies, enzymes, synthetic peptides, cell-penetrating peptide-drug conjugates, and RNAi sequences) in clinical developments for neuronal regeneration should benefit from the recent strategies for enhancement of their bioavailability. We highlight the advances in the development of nanoscale materials for drug delivery in neurodegenerative disorders. The emphasis is placed on nanoformulations for the delivery of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) using different types of lipidic nanocarriers (liposomes, liquid crystalline or solid lipid nanoparticles) and polymer-based scaffolds, nanofibers and hydrogels. Self-assembled soft-matter nanoscale materials show favorable neuroprotective characteristics, safety, and efficacy profiles in drug delivery to the central and peripheral nervous systems. The advances summarized here indicate that neuroprotective biomolecule-loaded nanoparticles and injectable hydrogels can improve neuronal survival and reduce tissue injury. Certain recently reported neuronal dysfunctions in long-COVID-19 survivors represent early manifestations of neurodegenerative pathologies. Therefore, BDNF delivery systems may also help in prospective studies on recovery from long-term COVID-19 neurological complications and be considered as promising systems for personalized treatment of neuronal dysfunctions and prevention or retarding of neurodegenerative disorders.
Keywords: biotherapeutics; brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF); lipid nanoparticles; nanocarriers; nanofibers; nanomedicine for growth factor delivery; neuroprotective assemblies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of the bibliography; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the work.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Dual and multi-drug delivery nanoparticles towards neuronal survival and synaptic repair.Neural Regen Res. 2017 Jun;12(6):886-889. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.208546. Neural Regen Res. 2017. PMID: 28761415 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacologically active microcarriers delivering BDNF within a hydrogel: Novel strategy for human bone marrow-derived stem cells neural/neuronal differentiation guidance and therapeutic secretome enhancement.Acta Biomater. 2017 Feb;49:167-180. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.11.030. Epub 2016 Nov 16. Acta Biomater. 2017. PMID: 27865962
-
Biofunctionalized peptide-based hydrogel as an injectable scaffold for BDNF delivery can improve regeneration after spinal cord injury.Injury. 2019 Feb;50(2):278-285. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2018.12.027. Epub 2018 Dec 19. Injury. 2019. PMID: 30595411
-
Temporally controlled growth factor delivery from a self-assembling peptide hydrogel and electrospun nanofibre composite scaffold.Nanoscale. 2017 Sep 21;9(36):13661-13669. doi: 10.1039/c7nr05004f. Nanoscale. 2017. PMID: 28876347
-
Recent Advances in Targeted Drug Delivery Approaches Using Lipidic and Polymeric Nanocarriers for the Management of Alzheimer's Disease.Curr Pharm Des. 2021;27(43):4388-4403. doi: 10.2174/1381612827666210927163258. Curr Pharm Des. 2021. PMID: 34579627 Review.
Cited by
-
Advanced Bioactive Polymers and Materials for Nerve Repair: Strategies and Mechanistic Insights.J Funct Biomater. 2025 Jul 9;16(7):255. doi: 10.3390/jfb16070255. J Funct Biomater. 2025. PMID: 40710469 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From Brain to Muscle: The Role of Muscle Tissue in Neurodegenerative Disorders.Biology (Basel). 2024 Sep 12;13(9):719. doi: 10.3390/biology13090719. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39336146 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurotrophic Factors as Regenerative Therapy for Neurodegenerative Diseases: Current Status, Challenges and Future Perspectives.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 15;24(4):3866. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043866. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transient Coatings from Nanoparticles Achieving Broad-Spectrum and High Antimicrobial Performance.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 May 30;16(6):816. doi: 10.3390/ph16060816. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37375764 Free PMC article.
-
Muscle Involvement in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Understanding the Pathogenesis and Advancing Therapeutics.Biomolecules. 2023 Oct 26;13(11):1582. doi: 10.3390/biom13111582. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 38002264 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
- CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/15_003/0000447 "Structural Dynamics of Biomolecular Systems" (ELIBIO)/European Regional Development Fund
- CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/16_019/0000789 "Advanced research using high-intensity laser produced photons and particles"/European Regional Development Fund
- 3+3 program, No. 204, item 27 from 25.03.2020/JINR, Dubna
- WIUCASQD2019005/Wenzhou Institute, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences
- 31670841/National Natural Science Foundation China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

