Expression and function of resolvin RvD1n-3 DPA receptors in oral epithelial cells
- PMID: 35808844
- PMCID: PMC9544308
- DOI: 10.1111/eos.12883
Expression and function of resolvin RvD1n-3 DPA receptors in oral epithelial cells
Abstract
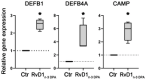
Chronic inflammatory responses can inflict permanent damage to host tissues. Specialized pro-resolving mediators downregulate inflammation but also can have other functions. The aim of this study was to examine whether oral epithelial cells express the receptors FPR2/ALX and DRV1/GPR32, which bind RvD1n-3 DPA , a recently described pro-resolving mediator derived from omega-3 docosapentaenoic acid (DPA), and whether RvD1n-3 DPA exposure induced significant responses in these cells. Gingival biopsies were stained using antibodies to FPR2/ALX and DRV1/GPR32. Expression of FPR2/ALX and DRV1/GPR32 was examined in primary oral epithelial cells by qRT-PCR, flow cytometry, and immunofluorescence. The effect of RvD1n-3 DPA on intracellular calcium mobilization and transcription of beta-defensins 1 and 2, and cathelicidin was evaluated by qRT-PCR. FPR2/ALX and DRV1/GPR32 were expressed by gingival keratinocytes in situ. In cultured oral epithelial cells, FPR2/ALX was detected on the cell surface, whereas FPR2/ALX and DRV1/GPR32 were detected intracellularly. Exposure to RvD1n-3 DPA induced intracellular calcium mobilization, FPR2/ALX internalization, DRV1/GPR32 translocation to the nucleus, and significantly increased expression of genes coding for beta-defensin 1, beta-defensin 2, and cathelicidin. This shows that the signal constituted by RvD1n-3 DPA is recognized by oral keratinocytes and that this can strengthen the antimicrobial and regulatory potential of the oral epithelium.
Keywords: DRV1/GPR32; FPR2/ALX; beta defensin; cathelicidin; oral epithelium.
© 2022 The Authors. European Journal of Oral Sciences published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Scandinavian Division of the International Association for Dental Research.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the authorship and publication of this article.
Figures



References
-
- Hasturk H, Kantarci A, Ohira T, Arita M, Ebrahimi N, Chiang N, et al. RvE1 protects from local inflammation and osteoclast‐mediated bone destruction in periodontitis. FASEB J. 2006;20:401–3. - PubMed
-
- Wijesinghe DS. Role of lipid mediators in diabetic wound healing. In: Bagchi D, Das A, Roy S, editors. Wound healing, tissue repair, and regeneration in diabetes. Cambridge: Academic Press; 2020. pp. 181–95.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

