Cytotoxic lesions of the corpus callosum after COVID-19 vaccination
- PMID: 35809100
- PMCID: PMC9282146
- DOI: 10.1007/s00234-022-03010-y
Cytotoxic lesions of the corpus callosum after COVID-19 vaccination
Abstract
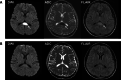
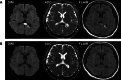
A 23-year-old previously healthy man (Patient 1) and a 33-year-old woman with a past history of depression (Patient 2) developed neurological symptoms approximately 1 week after receipt of the first COVID-19 mRNA vaccination and deteriorated over the next week. Patient 1 reported nausea, headache, a high fever, and retrograde amnesia. Patient 2 reported visual disturbance, headache, dysarthria, a left forearm tremor, dysesthesia of the mouth and distal limbs, and visual agnosia. PCR test results for SARS-CoV-2 were negative. Complete blood cell count, biochemistry, and antibody test and cerebrospinal fluid test findings were unremarkable. Diffusion-weighted and fluid-attenuated inversion recovery MRI of the brain showed a high signal intensity lesion at the midline of the splenium of the corpus callosum compatible with cytotoxic lesions of the corpus callosum (CLOCCs). High-dose intravenous methylprednisolone improved their symptoms and imaging findings. CLOCCs should be considered in patients with neurological manifestation after COVID-19 vaccination.
Keywords: COVID-19; COVID-19 mRNA vaccine; Coronavirus disease 2019; Cytotoxic lesions of the corpus callosum; Mild encephalitis/encephalopathy with reversible splenial lesion.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Before blaming a COVID vaccine for cytotoxic lesions of the corpus callosum all other differentials must be ruled out.Neuroradiology. 2022 Oct;64(10):1917-1918. doi: 10.1007/s00234-022-03022-8. Epub 2022 Jul 18. Neuroradiology. 2022. PMID: 35843986 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Response to: "Before blaming a COVID vaccine for cytotoxic lesions of the corpus callosum all other differentials must be ruled out".Neuroradiology. 2022 Nov;64(11):2101-2102. doi: 10.1007/s00234-022-03057-x. Epub 2022 Sep 23. Neuroradiology. 2022. PMID: 36138239 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Kim SS, Chang KH, Kim ST, et al. Focal lesion in the splenium of the corpus callosum in epileptic patients: antiepileptic drug toxicity? AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1999;20:125–129. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

