Genetic variation associated with condensate dysregulation in disease
- PMID: 35809564
- PMCID: PMC9339523
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2022.06.010
Genetic variation associated with condensate dysregulation in disease
Abstract
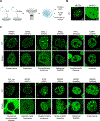
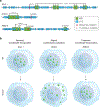
A multitude of cellular processes involve biomolecular condensates, which has led to the suggestion that diverse pathogenic mutations may dysregulate condensates. Although proof-of-concept studies have identified specific mutations that cause condensate dysregulation, the full scope of the pathological genetic variation that affects condensates is not yet known. Here, we comprehensively map pathogenic mutations to condensate-promoting protein features in putative condensate-forming proteins and find over 36,000 pathogenic mutations that plausibly contribute to condensate dysregulation in over 1,200 Mendelian diseases and 550 cancers. This resource captures mutations presently known to dysregulate condensates, and experimental tests confirm that additional pathological mutations do indeed affect condensate properties in cells. These findings suggest that condensate dysregulation may be a pervasive pathogenic mechanism underlying a broad spectrum of human diseases, provide a strategy to identify proteins and mutations involved in pathologically altered condensates, and serve as a foundation for mechanistic insights into disease and therapeutic hypotheses.
Keywords: Mendelian disease; biomolecular condensates; cancer; clinical genetics; condensate dysregulation; human genetics; pathogenic variants.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests R.A.Y. is a founder and shareholder of Syros Pharmaceuticals, Camp4 Therapeutics, Omega Therapeutics, and Dewpoint Therapeutics. S.F.B. and A.D. are consultants to Dewpoint Therapeutics. J.E.H. and O.O. are consultants to Camp4 Therapeutics. T.I.L. is a shareholder of Syros Pharmaceuticals and a consultant to Camp4 Therapeutics.
Figures


Comment in
-
Charting the human disease condensate dysregulome.Dev Cell. 2022 Jul 25;57(14):1677-1679. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2022.07.001. Dev Cell. 2022. PMID: 35901780
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

