Statin and aspirin as adjuvant therapy in hospitalised patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: a randomised clinical trial (RESIST trial)
- PMID: 35810307
- PMCID: PMC9270743
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-022-07570-5
Statin and aspirin as adjuvant therapy in hospitalised patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: a randomised clinical trial (RESIST trial)
Abstract
Background: Statins and aspirin have been proposed for treatment of COVID-19 because of their anti-inflammatory and anti-thrombotic properties. Several observational studies have shown favourable results. There is a need for a randomised controlled trial.
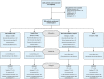
Methods: In this single-center, open-label, randomised controlled trial, 900 RT-PCR positive COVID-19 patients requiring hospitalisation, were randomly assigned to receive either atorvastatin 40 mg (Group A, n = 224), aspirin 75 mg (Group B, n = 225), or both (Group C, n = 225) in addition to standard of care for 10 days or until discharge whichever was earlier or only standard of care (Group D, n = 226). The primary outcome variable was clinical deterioration to WHO Ordinal Scale for Clinical Improvement ≥ 6. The secondary outcome was change in serum C-reactive protein, interleukin-6, and troponin I.
Results: The primary outcome occurred in 25 (2.8%) patients: 7 (3.2%) in Group A, 3 (1.4%) in Group B, 8 (3.6%) in Group C, and 7 (3.2%) in Group D. There was no difference in primary outcome across the study groups (P = 0.463). Comparison of all patients who received atorvastatin or aspirin with the control group (Group D) also did not show any benefit [Atorvastatin: HR 1.0 (95% CI 0.41-2.46) P = 0.99; Aspirin: HR 0.7 (95% CI 0.27-1.81) P = 0.46]. The secondary outcomes revealed lower serum interleukin-6 levels among patients in Groups B and C. There was no excess of adverse events.
Conclusions: Among patients admitted with mild to moderate COVID-19 infection, additional treatment with aspirin, atorvastatin, or a combination of the two does not prevent clinical deterioration. Trial Registry Number CTRI/2020/07/026791 ( http://ctri.nic.in ; registered on 25/07/2020).
Keywords: Aspirin; COVID-19; Serum IL-6; Statin; WHO ordinal scale.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
We declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Makris D, Manoulakas E, Komnos A, Papakrivou E, Tzovaras N, Hovas A, Zintzaras E, Zakynthinos E. Effect of pravastatin on the frequency of ventilator-associated pneumonia and on intensive care unit mortality: open-label, randomized study. Crit Care Med. 2011;39(11):2440–2446. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e318225742c. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Papazian L, Roch A, Charles PE, Penot-Ragon C, Perrin G, Roulier P, Goutorbe P, Lefrant JY, Wiramus S, Jung B, Perbet S, Hernu R, Nau A, Baldesi O, Allardet-Servent J, Baumstarck K, Jouve E, Moussa M, Hraiech S, Guervilly C, Forel JM. Effect of statin therapy on mortality in patients with ventilator-associated pneumonia: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2013;310(16):1692–1700. doi: 10.1001/jama.2013.280031. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

