Sildenafil improves radiation-induced oral mucositis by attenuating oxidative stress, NF-κB, ERK and JNK signalling pathways
- PMID: 35810384
- PMCID: PMC9357636
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.17480
Sildenafil improves radiation-induced oral mucositis by attenuating oxidative stress, NF-κB, ERK and JNK signalling pathways
Abstract
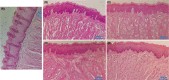
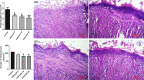
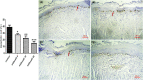
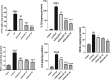
Radiation-induced oral mucositis is a common and dose-limiting complication of head and neck radiotherapy with no effective treatment. Previous studies revealed that sildenafil, a phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitor, has anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer effects. In this study, we investigated the effect of sildenafil on radiation-induced mucositis in rats. Two doses of radiation (8 and 26 Gy X-ray) were used to induce low-grade and high-grade oral mucositis, separately. A control group and three groups of sildenafil citrate-treated rats (5, 10, and 40 mg/kg/day) were used for each dose of radiation. Radiation increased MDA and activated NF-κB, ERK and JNK signalling pathways. Sildenafil significantly decreased MDA level, nitric oxide (NO) level, IL1β, IL6 and TNF-α. The most effective dose of sildenafil was 40 mg/kg/day in this study. Sildenafil also significantly inhibited NF-κB, ERK and JNK signalling pathways and increased bcl2/bax ratio. In addition, high-dose radiation severely destructed the mucosal layer in histopathology and led to mucosal cell apoptosis in the TUNEL assay. Sildenafil significantly improved mucosal structure and decreased inflammatory cell infiltration after exposure to high-dose radiation and reduced apoptosis in the TUNEL assay. These findings show that sildenafil can improve radiation-induced oral mucositis and decrease the apoptosis of mucosal cells via attenuation of inflammation and oxidative stress.
Keywords: apoptosis; inflammation; oxidative stress; radiation-induced oral mucositis; sildenafil.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sumatriptan alleviates radiation-induced oral mucositis in rats by inhibition of NF-kB and ERK activation, prevention of TNF-α and ROS release.Arch Oral Biol. 2020 Nov;119:104919. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2020.104919. Epub 2020 Sep 16. Arch Oral Biol. 2020. PMID: 32977152
-
A novel role of Nano selenium and sildenafil on streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy in rats by modulation of inflammatory, oxidative, and apoptotic pathways.Life Sci. 2022 Aug 15;303:120691. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120691. Epub 2022 Jun 4. Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35671809
-
Nrf2 and NF-қB interplay in tamoxifen-induced hepatic toxicity: A promising therapeutic approach of sildenafil and low-dose γ radiation.Environ Toxicol. 2023 May;38(5):990-996. doi: 10.1002/tox.23742. Epub 2023 Jan 30. Environ Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 36715126
-
NF-κB as a Potential Target for the Treatment and Prevention of Mucositis.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2023;24(13):1613-1622. doi: 10.2174/1389201024666230331121328. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36999705 Review.
-
The role of Smad7 in oral mucositis.Protein Cell. 2015 Mar;6(3):160-9. doi: 10.1007/s13238-014-0130-4. Epub 2015 Jan 8. Protein Cell. 2015. PMID: 25566830 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gasdermin D aggravates a mouse model of radiation-induced liver disease by promoting chemokine secretion and neutrophil recruitment.Nat Commun. 2025 Jul 2;16(1):6064. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-61397-7. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40603284 Free PMC article.
-
Sildenafil promotes osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells and inhibits bone loss by affecting the TGF-β signaling pathway.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025 Apr 23;16(1):201. doi: 10.1186/s13287-025-04320-7. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40264229 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted prevention of radiation-induced oral mucositis by glutathione-modified liposome coated K12 probiotics and clinical study.Mater Today Bio. 2025 Jul 29;34:102142. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.102142. eCollection 2025 Oct. Mater Today Bio. 2025. PMID: 40791797 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy of using metformin and/or quercetin for amelioration of gamma-irradiation induced tongue toxicity in diabetic rats.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Jan 18;24(1):110. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-03871-0. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 38238729 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the clinical efficacy and safety of Zhuhuang Powder combined with Qingyan Mixture in the prevention and treatment of radiation-induced oral mucositis: A retrospective cohort study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Aug 8;104(32):e43755. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000043755. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40797419 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ala M, Jafari RM, Ala M, et al. Sumatriptan alleviates radiation‐induced oral mucositis in rats by inhibition of NF‐kB and ERK activation, prevention of TNF‐α and ROS release. Arch Oral Biol. 2020;119:104919. - PubMed
-
- Moslemi D, Nokhandani AM, Otaghsaraei MT, Moghadamnia Y, Kazemi S, Moghadamnia AA. Management of chemo/radiation‐induced oral mucositis in patients with head and neck cancer: a review of the current literature. Radiother Oncol. 2016;120(1):13‐20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

