Lower levels of glutathione in the anterior cingulate cortex associate with depressive symptoms and white matter hyperintensities in COVID-19 survivors
- PMID: 35810586
- PMCID: PMC9239982
- DOI: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2022.06.008
Lower levels of glutathione in the anterior cingulate cortex associate with depressive symptoms and white matter hyperintensities in COVID-19 survivors
Abstract
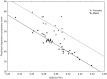
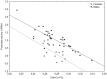
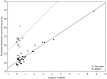
SARS-CoV-2 is a novel coronavirus that mainly affects the respiratory system. However, clinical manifestations such as neurological symptoms, psychopathological outcomes and brain alterations suggest brain involvement during SARS-CoV-2 infection. Depressive symptoms and cerebral white matter hypodensities/hyperintensities (WMH) have been widely reported in COVID-19 survivors and have been shown to persist after recovery from infection. At the same time viral Infections, including COVID-19, have been shown to lead to oxidative stress. Glutathione (GSH) is the main antioxidant in the brain and reduced GSH levels have been implicated both in COVID-19 and depression. We therefore hypothesise that reduced GSH levels may be associated with depressive symptoms and WMH in COVID-19 survivors. Forty-nine participants (age 18-70) surviving COVID-19 underwent magnetic resonance imaging to measure WMH and brain GSH levels in the ACC, blood sampling to measure systemic inflammation and psychopathological assessment for depressive symptoms. ACC concentrations of GSH inversely associated with both depression scores and the number and volume of WMH. The volume of WMH also positively associated with depressive symptomatology. Finally, systemic inflammation negatively predicted GSH concentration in ACC. In conclusion, we observed overlapping associations of GSH levels in ACC, WMH and severity of depression in COVID-19 survivors, and confirmed the central role of systemic inflammation, thus warranting interest for further study of oxidative stress and antioxidants in the post-acute COVID-19 syndrome.
Keywords: COVID-19; Depression; GSH; SARS-COV-2; Spectroscopy; White matter.
Copyright © 2022. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest None.
Figures
References
-
- Benedetti F., Palladini M., Paolini M., Melloni E., Vai B., De Lorenzo R., Furlan R., Rovere-Querini P., Falini A., Mazza M.G. Brain correlates of depression, post-traumatic distress, and inflammatory biomarkers in COVID-19 survivors: a multimodal magnetic resonance imaging study. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2021 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boroujeni M.E., Simani L., Bluyssen H.A.R., Samadikhah H.R., Zamanlui Benisi S., Hassani S., Akbari Dilmaghani N., Fathi M., Vakili K., Mahmoudiasl G.R., Abbaszadeh H.A., Hassani Moghaddam M., Abdollahifar M.A., Aliaghaei A. Inflammatory Response Leads to Neuronal Death in Human Post-Mortem Cerebral Cortex in Patients with COVID-19. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2021;12:2143–2150. - PubMed
-
- Czarny P., Wigner P., Galecki P., Sliwinski T. The interplay between inflammation, oxidative stress, DNA damage, DNA repair and mitochondrial dysfunction in depression. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry. 2018;80:309–321. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

