A dorsal CA2 to ventral CA1 circuit contributes to oxytocinergic modulation of long-term social recognition memory
- PMID: 35811321
- PMCID: PMC9272559
- DOI: 10.1186/s12929-022-00834-x
A dorsal CA2 to ventral CA1 circuit contributes to oxytocinergic modulation of long-term social recognition memory
Abstract
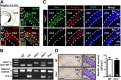
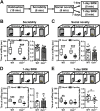
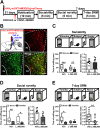
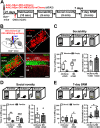
Background: Social recognition memory (SRM) is the ability to distinguish familiar from novel conspecifics and is crucial for survival and reproductive success across social species. We previously reported that oxytocin (OXT) receptor (OXTR) signaling in the CA2/CA3a of dorsal hippocampus is essential to promote the persistence of long-term SRM, yet how the endogenous OXT system influences CA2 outputs to regulate long-term SRM formation remains unclear.
Methods: To achieve a selective deletion of CA2 OXTRs, we crossed Amigo2-Cre mice with Oxtr-floxed mice to generate CA2-specific Oxtr conditional knockout (Oxtr-/-) mice. A three-chamber paradigm test was used for studying SRM in mice. Chemogenetic and optogenetic targeting strategies were employed to manipulate neuronal activity.
Results: We show that selective ablation of Oxtr in the CA2 suffices to impair the persistence of long-term SRM but has no effect on sociability and social novelty preference in the three-chamber paradigm test. We find that cell-type specific activation of OXT neurons within the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus enhances long-term SRM and this enhancement is blocked by local application of OXTR antagonist L-368,899 into dorsal hippocampal CA2 (dCA2) region. In addition, chemogenetic neuronal silencing in dCA2 demonstrated that neuronal activity is essential for forming long-term SRM. Moreover, chemogenetic terminal-specific inactivation reveals a crucial role for dCA2 outputs to ventral CA1 (vCA1), but not dorsal lateral septum, in long-term SRM. Finally, targeted activation of the dCA2-to-vCA1 circuit effectively ameliorates long-term SRM deficit observed in Oxtr-/- mice.
Conclusions: These findings highlight the importance of hippocampal CA2 OXTR signaling in governing the persistence of long-term SRM and identify a hippocampal circuit linking dCA2 to vCA1 necessary for controlling long-term SRM formation.
Keywords: CA2; Hippocampus; Oxytocin; Oxytocin receptor; Paraventricular nucleus; Social recognition memory.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Conditional Deletion of Hippocampal CA2/CA3a Oxytocin Receptors Impairs the Persistence of Long-Term Social Recognition Memory in Mice.J Neurosci. 2018 Jan 31;38(5):1218-1231. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1896-17.2017. Epub 2017 Dec 26. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29279308 Free PMC article.
-
Oxytocin Receptors Are Expressed by Glutamatergic Prefrontal Cortical Neurons That Selectively Modulate Social Recognition.J Neurosci. 2019 Apr 24;39(17):3249-3263. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2944-18.2019. Epub 2019 Feb 25. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30804095 Free PMC article.
-
Oxytocin-Modulated Ion Channel Ensemble Controls Depolarization, Integration and Burst Firing in CA2 Pyramidal Neurons.J Neurosci. 2022 Oct 12;42(41):7707-7720. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0921-22.2022. Epub 2022 Sep 8. J Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36414006 Free PMC article.
-
Oxytocin receptor signaling in the hippocampus: Role in regulating neuronal excitability, network oscillatory activity, synaptic plasticity and social memory.Prog Neurobiol. 2018 Dec;171:1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2018.10.003. Epub 2018 Oct 22. Prog Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 30359747 Review.
-
The oxytocin receptor represents a key hub in the GPCR heteroreceptor network: potential relevance for brain and behavior.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 Dec 8;15:1055344. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.1055344. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36618821 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Social odors drive hippocampal CA2 place cell responses to social stimuli.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 19:2024.07.16.603738. doi: 10.1101/2024.07.16.603738. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Prog Neurobiol. 2025 Feb;245:102708. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2024.102708. PMID: 39071428 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
The Role of Oxytocin in Abnormal Brain Development: Effect on Glial Cells and Neuroinflammation.Cells. 2022 Dec 2;11(23):3899. doi: 10.3390/cells11233899. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36497156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxytocin modulates inhibitory balance in the prelimbic cortex to support social memory consolidation during REM sleep.Theranostics. 2025 Feb 18;15(8):3257-3274. doi: 10.7150/thno.109104. eCollection 2025. Theranostics. 2025. PMID: 40093885 Free PMC article.
-
Linking Social Cognition, Parvalbumin Interneurons, and Oxytocin in Alzheimer's Disease: An Update.J Alzheimers Dis. 2023;96(3):861-875. doi: 10.3233/JAD-230333. J Alzheimers Dis. 2023. PMID: 37980658 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Social odors drive hippocampal CA2 place cell responses to social stimuli.Prog Neurobiol. 2025 Feb;245:102708. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2024.102708. Epub 2024 Dec 30. Prog Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 39743170 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Okuyama T, Yokoi S, Abe H, Isoe Y, Suehiro Y, Imada H, et al. A neural mechanism underlying mating preferences for familiar individuals in medaka fish. Science. 2014;343(6166):91–94. - PubMed
-
- Ferguson JN, Young LJ, Insel TR. The neuroendocrine basis of social recognition. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2002;23(2):200–224. - PubMed
-
- Jacobs SA, Huang F, Tsien JZ, Wei W. Social recognition memory test in rodents. Bio Protoc. 2016;6:e1804.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- NHRI-EX110-10912NI/National Health Research Institute, Taiwan
- NHRI-EX111-10912NI/National Health Research Institute, Taiwan
- 107-2320-B-006-037-MY3/Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan
- 109-2320-B-006-039-MY3/Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan
- 110-2331-B-006-036-MY3/Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

