Fatty Liver Index Independently Predicts All-Cause Mortality in Patients With Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis but No Substantial Liver Disease
- PMID: 35811721
- PMCID: PMC9259888
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.848121
Fatty Liver Index Independently Predicts All-Cause Mortality in Patients With Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis but No Substantial Liver Disease
Abstract
Background: This study investigated whether the fatty liver index (FLI) could predict all-cause mortality and cerebrovascular accident (CVA) during follow-up in patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis (AAV) without substantial liver disease.
Methods: The medical records of 75 AAV patients with AAV were retrospectively reviewed. An equation for the FLI is as follows: FLI = (e0.953×loge(triglycerides)+0.139×BMI+0.718×loge(GGT)+0.053×waistcircumference-15.745)/(1 + e0.953×loge(triglycerides)+0.139×BMI+0.718×loge(GGT)+0.053×waistcircumference-15.745) × 100. The cut-offs of the FLI were obtained using the receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curve analysis.
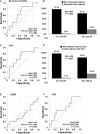
Results: The mean age at AAV diagnosis was 59.1 years and 42.7% were male. Eight patients (10.7%) died and 8 patients had CVA during follow-up. When the cut-offs of the FLI for all-cause mortality and CVA were set as the FLI ≥ 33.59 and the FLI ≥ 32.31, AAV patients with the FLI over each cut-off exhibited a higher risk for all-cause mortality or CVA than those without (RR 8.633 and 8.129), respectively. In addition, AAV patients with the FLI over each cut-off exhibited a significantly lower cumulative patients' survival rate or CVA-free survival rate than those without, respectively. In the multivariable Cox analysis, only the FLI ≥ 33.59 at AAV diagnosis was an independent predictor of all-cause mortality during follow-up in AAV patients (HR 10.448).
Conclusion: The FLI at AAV diagnosis can be a potential independent predictor of all-cause mortality and CVA during follow-up in AAV patients. We suggest that physicians measure the FLI at AAV diagnosis and pay more attention to those with a high FLI value for prevention of future mortality and CVA.
Keywords: antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody; cerebrovascular accident; fatty liver index; mortality; vasculitis.
Copyright © 2022 Park, Pyo, Ahn, Choi, Song, Park, Huh and Lee.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Watts R, Lane S, Hanslik T, Hauser T, Hellmich B, Koldingsnes W, et al. Development and validation of a consensus methodology for the classification of the ANCA-associated vasculitides and polyarteritis nodosa for epidemiological studies. Ann Rheum Dis. (2007) 66:222–7. 10.1136/ard.2006.054593 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

