Preparation, characterization, and antibacterial activity of plaunotol and plaunoi extracts complexed with hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin
- PMID: 35812138
- PMCID: PMC9257859
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsps.2022.04.004
Preparation, characterization, and antibacterial activity of plaunotol and plaunoi extracts complexed with hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin
Abstract
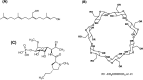
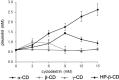
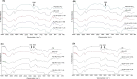
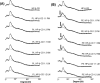
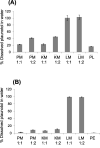
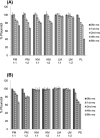
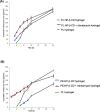
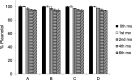
Croton stellatopilosus (Plaunoi) leaves accumulate several diterpenes and possess various pharmacological activities. The present study aimed to prepare, characterize and assess the antibacterial activity of inclusion complexes prepared by mixing plaunotol (PL) or plaunoi extract (PE) with cyclodextrins (CD), including α-CD, β-CD, γ-CD, and hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HP-β-CD). The inclusion complexes were characterized using SEM, XRD, DSC, and FT-IR and evaluated for aqueous solubility and thermal stability. The PL and PE lyophilized complexes with HP-β-CD were further evaluated for their antibacterial activity against acne-causing bacteria. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and the minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) of PL, PE, and the inclusion complexes evaluated using the agar dilution method revealed that the MIC and MBC values of the inclusion complexes were lower than those of PL or PE alone. Interestingly, the complexes had a synergistic activity with clindamycin after testing with checkerboard assay. The hydrogel containing the inclusion complex and clindamycin were assessed for antibacterial activity using the agar well diffusion method. The results indicated that the hydrogels showed significant inhibition of bacterial growth. In conclusion, the prepared solid dispersion of PL or PE with HP-β-CD could enhance antibacterial activity by increasing the drug solubility. The hydrogels containing PL or PE complex and clindamycin could be considered as a candidate for the treatment of acne vulgaris.
Keywords: Antibacterial activity; CD, cyclodextrin; DSC, Differential scanning calorimetry; FICI, fractional inhibitory concentration index; FT-IR, Fourier-transformed infrared spectrometry; HP-β-CD, hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin; Hydrogel; Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin; Inclusion complex; KM, kneading method; LM, lyophilized method; MBC, minimal bactericidal concentration; MIC, minimal inhibitory concentration; PE, plaunoi extract; PE:HP-β-CD, inclusion complex of plaunoi extract and hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin; PL, plaunotol; PL:HP-β-CD, inclusion complex of plaunotol and hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin; PM, physical mixture; Plaunoi extract; Plaunotol; SEM, scanning electron microscope; XRD, X-ray diffraction.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Aelenei P., Rimbu C.M., Horhogea C.E., Lobiuc A., Neagu A.N., Dunca S.I., Motrescu I., Dimitriu G., Aprotosoaie A.C., Miron A. Prenylated phenolics as promising candidates for combination antibacterial therapy: morusin and kuwanon G. Saudi Pharm. J. 2020;28:1172–1181. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2020.08.006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aswathy, S.H., Narendrakumar, U., Manjubala, I., 2020. Commercial hydrogels for biomedical applications. Heliyon. 6, e03719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03719. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aung W.M., Limsuwanchote S., Wungsintaweekul J. Preparation of diterpenes-enriched extract from Croton stellatopilosus ohba leaves using enzyme- and ultrasonic-assisted extraction. Phcog Res. 2021;13(1):22.
-
- Bukhari, S.M.H., Khan, S., Rehanullah, M., Ranjha, N.M., 2015. Synthesis and characterization of chemically cross-linked acrylic acid/gelatin hydrogels: effect of pH and composition on swelling and drug release. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2015, 187961. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/187961.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

