Transient Response and Firing Behaviors of Memristive Neuron Circuit
- PMID: 35812218
- PMCID: PMC9257141
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2022.922086
Transient Response and Firing Behaviors of Memristive Neuron Circuit
Abstract
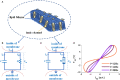
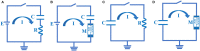
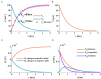
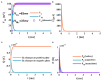
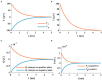
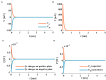
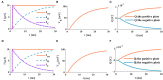
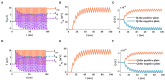
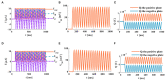
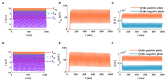
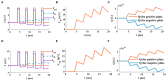
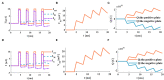
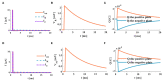
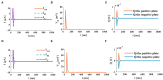
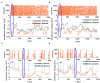
The signal transmission mechanism of the Resistor-Capacitor (RC) circuit is similar to the intracellular and extracellular signal propagating mechanism of the neuron. Thus, the RC circuit can be utilized as the circuit model of the neuron cell membrane. However, resistors are electronic components with the fixed-resistance and have no memory properties. A memristor is a promising neuro-morphological electronic device with nonvolatile, switching, and nonlinear characteristics. First of all, we consider replacing the resistor in the RC neuron circuit with a memristor, which is named the Memristor-Capacitor (MC) circuit, then the MC neuron model is constructed. We compare the charging and discharging processes between the RC and MC neuron circuits. Secondly, two models are compared under the different external stimuli. Finally, the synchronous and asynchronous activities of the RC and MC neuron circuits are performed. Extensive experimental results suggest that the charging and discharging speed of the MC neuron circuit is faster than that of the RC neuron circuit. Given sufficient time and proper external stimuli, the RC and MC neuron circuits can produce the action potentials. The synchronous and asynchronous phenomena in the two neuron circuits reproduce nonlinear dynamic behaviors of the biological neurons.
Keywords: MC circuit; RC circuit; firing behaviors; memristor; neuron.
Copyright © 2022 Fang, Tan, Zhang, Duan and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Coherence resonance and energy dynamics in a memristive map neuron.Chaos. 2025 Feb 1;35(2):023158. doi: 10.1063/5.0251352. Chaos. 2025. PMID: 39983736
-
Memristor Circuits for Simulating Neuron Spiking and Burst Phenomena.Front Neurosci. 2021 Jun 10;15:681035. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.681035. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34177457 Free PMC article.
-
Memristive Izhikevich Spiking Neuron Model and Its Application in Oscillatory Associative Memory.Front Neurosci. 2022 May 3;16:885322. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.885322. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35592261 Free PMC article.
-
A memristive neuron and its adaptability to external electric field.Chaos. 2023 Feb;33(2):023110. doi: 10.1063/5.0136195. Chaos. 2023. PMID: 36859211
-
Review on Excess Noise Measurements of Resistors.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Jan 18;23(3):1107. doi: 10.3390/s23031107. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36772146 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adapa A. K., Bhowmick S., John V. (2020). Low-frequency dc-link capacitor current mitigation in reduced switch count single-phase to three-phase converter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 68, 3058–3068. 10.1109/TIE.2020.2977543 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

