Myostatin and its Regulation: A Comprehensive Review of Myostatin Inhibiting Strategies
- PMID: 35812316
- PMCID: PMC9259834
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2022.876078
Myostatin and its Regulation: A Comprehensive Review of Myostatin Inhibiting Strategies
Abstract
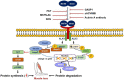
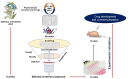
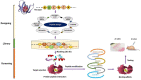
Myostatin (MSTN) is a well-reported negative regulator of muscle growth and a member of the transforming growth factor (TGF) family. MSTN has important functions in skeletal muscle (SM), and its crucial involvement in several disorders has made it an important therapeutic target. Several strategies based on the use of natural compounds to inhibitory peptides are being used to inhibit the activity of MSTN. This review delivers an overview of the current state of knowledge about SM and myogenesis with particular emphasis on the structural characteristics and regulatory functions of MSTN during myogenesis and its involvements in various muscle related disorders. In addition, we review the diverse approaches used to inhibit the activity of MSTN, especially in silico approaches to the screening of natural compounds and the design of novel short peptides derived from proteins that typically interact with MSTN.
Keywords: MSTN inhibitors; myostatin; natural compounds; peptides; skeletal muscle.
Copyright © 2022 Baig, Ahmad, Moon, Park, Ho Lim, Chun, Qadri, Hwang, Jan, Ahmad, Ali, Shaikh, Lee and Choi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Allen D. L., Cleary A. S., Speaker K. J., Lindsay S. F., Uyenishi J., Reed J. M., et al. (2008). Myostatin, Activin Receptor IIb, and Follistatin-Like-3 Gene Expression Are Altered in Adipose Tissue and Skeletal Muscle of Obese Mice. Am. J. Physiology-Endocrinology Metabolism 294, E918–E927. 10.1152/ajpendo.00798.2007 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

