Assessment of the safety of the cationic arginine-rich peptides (CARPs) poly-arginine-18 (R18 and R18D) in ex vivo models of mast cell degranulation and red blood cell hemolysis
- PMID: 35812346
- PMCID: PMC9257347
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2022.101305
Assessment of the safety of the cationic arginine-rich peptides (CARPs) poly-arginine-18 (R18 and R18D) in ex vivo models of mast cell degranulation and red blood cell hemolysis
Abstract
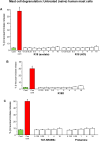
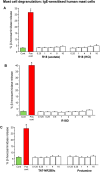
Our laboratory focuses on the development of novel neuroprotective cationic peptides, such poly-arginine-18 (R18: 18-mer of l-arginine; net charge +18) and its d-enantiomer R18D in stroke and other brain injuries. In the clinical development of R18/R18D, their cationic property raises potential safety concerns on their non-specific effects to induce mast cell degranulation and hemolysis. To address this, we first utilised primary human cultured mast cells (HCMCs) to examine anaphylactoid effects. We also included as controls, the well-characterised neuroprotective TAT-NR2B9c peptide and the widely used heparin reversal peptide, protamine. Degranulation assay based on β-hexosaminidase release demonstrated that R18 and R18D did not induce significant mast cell degranulation in both untreated (naïve) and IgE-sensitised HCMCs in a dose-response study to a maximum peptide concentration of 16 μM. Similarly, TAT-NR2B9c and protamine did not induce significant mast cell degranulation. To examine hemolytic effects, red blood cells (RBCs), were incubated with the peptides at a concentration range of 1-16 μM in the absence or presence of 2% plasma. Measurement of hemoglobin absorbance revealed that only R18 induced a modest, but significant degree of hemolysis at the 16 μM concentration, and only in the absence of plasma. This study addressed the potential safety concern of the application of the cationic neuroprotective peptides, especially, R18D, on anaphylactoid responses and hemolysis. The findings indicate that R18, R18D, TAT-NR2B9c and protamine are unlikely to induce histamine mediated anaphylactoid reactions or RBC hemolysis when administered intravenously to patients.
Keywords: Cationic arginine-rich peptides; Hemolysis; Mast cells degranulation; Polyarginine-18 (R18); Protamine; TAT-NR2B9c.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
N.K and B.M are named inventors on several patents for the use of CARPs as therapeutic agents. In addition, N.K, B.M and A.E are shareholders of Argenica Therapeutics, which is a company developing R18 as a stroke therapeutic. D.Y and F.M have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of neuroprotective efficacy of poly-arginine R18 and R18D (D-enantiomer) peptides following permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in the Wistar rat and in vitro toxicity studies.PLoS One. 2018 Mar 7;13(3):e0193884. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0193884. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29513757 Free PMC article.
-
Poly-arginine R18 and R18D (D-enantiomer) peptides reduce infarct volume and improves behavioural outcomes following perinatal hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy in the P7 rat.Mol Brain. 2018 Feb 9;11(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s13041-018-0352-0. Mol Brain. 2018. PMID: 29426351 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Assessment of the Proteolytic Stability and Impact of Poly-Arginine Peptides R18 and R18D on Infarct Growth and Penumbral Tissue Preservation Following Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion in the Sprague Dawley Rat.Neurochem Res. 2021 May;46(5):1166-1176. doi: 10.1007/s11064-021-03251-y. Epub 2021 Feb 1. Neurochem Res. 2021. PMID: 33523394
-
Neuroprotective Cationic Arginine-Rich Peptides (CARPs): An Assessment of Their Clinical Safety.Drug Saf. 2020 Oct;43(10):957-969. doi: 10.1007/s40264-020-00962-z. Drug Saf. 2020. PMID: 32613595 Review.
-
Perinatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy and Neuroprotective Peptide Therapies: A Case for Cationic Arginine-Rich Peptides (CARPs).Brain Sci. 2018 Aug 7;8(8):147. doi: 10.3390/brainsci8080147. Brain Sci. 2018. PMID: 30087289 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Membrane-Active Peptides and Their Potential Biomedical Application.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Aug 6;15(8):2091. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15082091. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37631305 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell-Penetrating and Enzyme-Responsive Peptides for Targeted Cancer Therapy: Role of Arginine Residue Length on Cell Penetration and In Vivo Systemic Toxicity.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024 Mar 6;16(9):11159-11171. doi: 10.1021/acsami.3c14908. Epub 2024 Feb 22. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024. PMID: 38385360 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Meloni B., et al. Neuroprotective peptides fused to arginine-rich cell penetrating peptides: neuroprotective mechanism likely mediated by peptide endocytic properties. Pharmacol. Ther. Sep. 2015;153:36–54. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

