Sustainable irrigation technologies: a water-energy-food (WEF) nexus perspective towards achieving more crop per drop per joule per hectare
- PMID: 35812360
- PMCID: PMC9254736
- DOI: 10.1088/1748-9326/ac7b39
Sustainable irrigation technologies: a water-energy-food (WEF) nexus perspective towards achieving more crop per drop per joule per hectare
Abstract
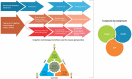
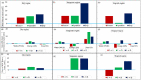
Sustainable agricultural intensification requires irrigation methods and strategies to minimize yield penalties while optimizing water, land and energy use efficiencies. We assessed, from a silo-based and integrated water-energy-food (WEF) nexus perspective, the performance of irrigation technologies in different agro-climatic regions. Secondary to this, we assessed the impact of adopting systematic approaches such as the WEF nexus on improving efficiency in irrigated agriculture through irrigation modernization. The evidence-based perspectives of silo-based performances individually considered the metrics of yield (Y), water use efficiency (WUE), and energy productivity (EP). The WEF nexus approach applied sustainability polygons to integrate the three metrics into a nexus index representing the holistic performance of the irrigation technologies. Silo-based performance in temperate regions suggests net gains for WUE (+1.10 kg m-3) and Y (+6.29 ton ha-1) when transitioning from furrow to sprinkler irrigation, with a net loss in EP (-3.82 ton MJ-1). There is potential for a net loss on EP (-3.33 ton MJ-1) when transitioning from furrow to drip system in temperate regions. The best performance of irrigation technologies in dry regions in water, energy and food silos was achieved by sprinkler, drip and furrow irrigation systems, respectively. Thus, appraising irrigation technologies from a silos perspective promotes individual silos, which renders an unsustainable picture of the performance of irrigation systems. The integrative WEF nexus approach successfully highlighted the trade-offs and synergies in the nexus of water, energy and food in irrigated agriculture. Drip irrigation led all irrigation technologies in WEF nexus performance in dry (21.44 unit2), tropical (23.98 unit2), and temperate regions (47.28 unit2). Overall, the irrigation modernization pathway to drip technology from either furrow or sprinkler systems improves irrigated agriculture's WEF nexus performance in all three regions for more crop per drop per joule per hectare under climate change. This can promote inclusive and sustainable irrigation development within the planetary boundaries.
Keywords: agricultural water management; integrated; irrigation modernization; resilience; silo; trade-offs; water-energy-food nexus.
© 2022 The Author(s). Published by IOP Publishing Ltd.
Figures


Similar articles
-
An African perspective on the Water-Energy-Food nexus.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 6;13(1):16842. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-43606-9. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37803054 Free PMC article.
-
Advancing irrigation management: integrating technology and sustainability to address global food security.Environ Monit Assess. 2024 Oct 5;196(11):1018. doi: 10.1007/s10661-024-13145-5. Environ Monit Assess. 2024. PMID: 39367142 Review.
-
Climate Change Adaptation through the Water-Energy-Food Nexus in Southern Africa.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018 Oct 19;15(10):2306. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15102306. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018. PMID: 30347771 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A systematic analysis of Water-Energy-Food security nexus: A South Asian case study.Sci Total Environ. 2020 Aug 1;728:138451. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138451. Epub 2020 Apr 22. Sci Total Environ. 2020. PMID: 32570309
-
The Water-Energy-Food Nexus as a Tool to Transform Rural Livelihoods and Well-Being in Southern Africa.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Aug 18;16(16):2970. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16162970. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31426610 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Integrated assessment of irrigation and agriculture management challenges in Nepal: An interdisciplinary perspective.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 10;10(9):e29407. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29407. eCollection 2024 May 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38698972 Free PMC article.
-
Embracing complexities in agricultural water management through nexus planning.Irrig Drain. 2024 Nov;73(5):1695-1716. doi: 10.1002/ird.3041. Epub 2024 Sep 29. Irrig Drain. 2024. PMID: 40092646 Free PMC article.
-
Why Do Farmers Not Irrigate All the Areas Equipped for Irrigation? Lessons from Southern Africa.Agriculture (Basel). 2024 Jul 24;14(8):1218. doi: 10.3390/agriculture14081218. Agriculture (Basel). 2024. PMID: 40092322 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ADB . Manila: 2017. Quantifying water and energy linkages in irrigation—experiences from Viet Nam. - DOI
-
- Afzalinia S, Ziaee A R. Effect of Conservation Tillage and Irrigation Methods on the Cotton Yield and Water Use Efficiency. Leuven: International Society for Horticultural Science (ISHS); 2014. pp. 119–26. - DOI
-
- AL-agele H A, Nackley L, Higgins C W. A pathway for sustainable agriculture. Sustainability. 2021;13:4328. doi: 10.3390/su13084328. - DOI
-
- Banaeian N, Zangeneh M, Clark S. Trends and future directions in crop energy analyses: a focus on Iran. Sustainability. 2020;12:10002. doi: 10.3390/su122310002. - DOI
-
- Beekma J, et al. Enabling policy environment for water, food and energy security. Irrig. Drain. 2021;70:392–409. doi: 10.1002/ird.2560. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
