3D Genome Organization as an Epigenetic Determinant of Transcription Regulation in T Cells
- PMID: 35812421
- PMCID: PMC9257000
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.921375
3D Genome Organization as an Epigenetic Determinant of Transcription Regulation in T Cells
Abstract
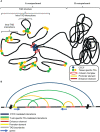
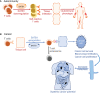
In the heart of innate and adaptive immunity lies the proper spatiotemporal development of several immune cell lineages. Multiple studies have highlighted the necessity of epigenetic and transcriptional regulation in cell lineage specification. This mode of regulation is mediated by transcription factors and chromatin remodelers, controlling developmentally essential gene sets. The core of transcription and epigenetic regulation is formulated by different epigenetic modifications determining gene expression. Apart from "classic" epigenetic modifications, 3D chromatin architecture is also purported to exert fundamental roles in gene regulation. Chromatin conformation both facilitates cell-specific factor binding at specified regions and is in turn modified as such, acting synergistically. The interplay between global and tissue-specific protein factors dictates the epigenetic landscape of T and innate lymphoid cell (ILC) lineages. The expression of global genome organizers such as CTCF, YY1, and the cohesin complexes, closely cooperate with tissue-specific factors to exert cell type-specific gene regulation. Special AT-rich binding protein 1 (SATB1) is an important tissue-specific genome organizer and regulator controlling both long- and short-range chromatin interactions. Recent indications point to SATB1's cooperation with the aforementioned factors, linking global to tissue-specific gene regulation. Changes in 3D genome organization are of vital importance for proper cell development and function, while disruption of this mechanism can lead to severe immuno-developmental defects. Newly emerging data have inextricably linked chromatin architecture deregulation to tissue-specific pathophysiological phenotypes. The combination of these findings may shed light on the mechanisms behind pathological conditions.
Keywords: SATB1; adaptive immunity; autoimmunity; epigenetics; genome organization; thymocyte development.
Copyright © 2022 Papadogkonas, Papamatheakis and Spilianakis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SATB1 regulates 3D genome architecture in T cells by constraining chromatin interactions surrounding CTCF-binding sites.Cell Rep. 2023 Apr 25;42(4):112323. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112323. Epub 2023 Mar 30. Cell Rep. 2023. PMID: 37000624
-
The 3D enhancer network of the developing T cell genome is shaped by SATB1.Nat Commun. 2022 Nov 14;13(1):6954. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34345-y. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36376298 Free PMC article.
-
SATB1 prevents immune cell infiltration by regulating chromatin organization and gene expression of a chemokine gene cluster in T cells.Commun Biol. 2024 Oct 11;7(1):1304. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-07021-8. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39394451 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin organizer SATB1 as a novel molecular target for cancer therapy.Curr Drug Targets. 2012 Dec;13(13):1603-15. doi: 10.2174/138945012803530008. Curr Drug Targets. 2012. PMID: 22998183 Review.
-
Multi-Dimensional Gene Regulation in Innate and Adaptive Lymphocytes: A View From Regulomes.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 25;12:655590. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.655590. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33841440 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deciphering the TET3 interactome in primary thymic developing T cells.iScience. 2024 Apr 18;27(5):109782. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109782. eCollection 2024 May 17. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38711449 Free PMC article.
-
3D genome perspective on cell fate determination, organ regeneration, and diseases.Cell Prolif. 2023 May;56(5):e13482. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13482. Epub 2023 May 17. Cell Prolif. 2023. PMID: 37199020 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Concomitant loss of TET2 and TET3 results in T cell expansion and genomic instability in mice.Commun Biol. 2024 Dec 3;7(1):1606. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-07312-0. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39627458 Free PMC article.
-
SATB1 in cancer progression and metastasis: mechanisms and therapeutic potential.Front Oncol. 2025 Feb 25;15:1535929. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1535929. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40071088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Environmental exposures influence multigenerational epigenetic transmission.Clin Epigenetics. 2024 Oct 17;16(1):145. doi: 10.1186/s13148-024-01762-3. Clin Epigenetics. 2024. PMID: 39420431 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

