Effect of Exercise Training on Body Composition and Inflammatory Cytokine Levels in Overweight and Obese Individuals: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 35812437
- PMCID: PMC9260601
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.921085
Effect of Exercise Training on Body Composition and Inflammatory Cytokine Levels in Overweight and Obese Individuals: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to compare and rank the effectiveness of aerobic exercise (AE), resistance training (RT), combined aerobic and resistance training (CT), and high-intensity interval training (HIIT) on body composition and inflammatory cytokine levels in overweight and obese individuals by using network meta-analysis (NMA).
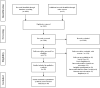
Methods: We searched the PubMed, Cochrane, Embase, Web of Science, and EBSCO databases to identify randomized controlled trials investigating the effects of exercise training on inflammatory cytokines in overweight and obese patients. The retrieval period was from inception to November 2021. Two reviewers independently screened the retrieved articles, extracted the pertinent data, and assessed the risk of bias of the included studies; then, they used Stata 16.0 and Review Manager 5.3 to perform an NMA.
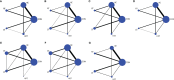
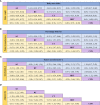
Results: A total of 38 studies involving 1317 patients were included in this study. The results of the NMA indicated that AE had the greatest effect on weight loss (SUCRA=78.3; SMD=-0.51, 95% CI: -0.70, -0.33); CT had the greatest effect on reducing body mass index (SUCRA=70.7; SMD=-0.46, 95% CI: -0.81, -0.10), waist circumference (SUCRA=93.4; SMD=-1.86, 95% CI: -2.80, -0.93), percentage body fat (SUCRA=79.6; SMD=-1.38, 95% CI: -2.29, -0.48), interleukin-6 level (SUCRA=86.4; SMD=-1.98, 95% CI: -3.87, -0.09), and tumor necrosis factor-α level (SUCRA=79.4; SMD=-2.08, 95% CI: -3.75, -0.42); AE (SMD=0.51, 95% CI: -1.68, 2.69), RT (SMD=0.15, 95% CI: -3.01, 3.32), CT (SMD=1.78, 95% CI: -1.35, 4.92), and HIIT (SMD=2.29, 95% CI: -1.27, 5.86) did not significantly increase the adiponectin level.
Conclusion: The current results suggest that CT is the best exercise modality for improving body composition and inflammatory status in overweight and obese individuals. More rigorous randomized control trials are needed for further validation.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/, identifier CRD42022303165.
Keywords: body composition; exercise; inflammatory cytokine; network meta-analysis; overweight and obese individuals.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Zhou, Zhao and He.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Di Cesare M, Bentham J, Stevens GA, Zhou B, Danaei G, Lu Y, et al. Trends in Adult Body-Mass Index in 200 Countries From 1975 to 2014: A Pooled Analysis of 1698 Population-Based Measurement Studies With 19·2 Million Participants. Lancet (2016) 387(10026):1377–96. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(16)30054-x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

