Are There Any Cardioprotective Effects or Safety Concerns of Erythropoietin in Patients With Myocardial Infarction? A Systematic Review
- PMID: 35812547
- PMCID: PMC9255911
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.25671
Are There Any Cardioprotective Effects or Safety Concerns of Erythropoietin in Patients With Myocardial Infarction? A Systematic Review
Abstract
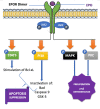
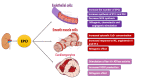
Myocardial infarction (MI) is a global cause of morbidity and mortality. MI is the outcome of a chronic process termed atherosclerosis, a buildup of fatty and other substances called plaques inside the coronary vessels, causing hardening and thickening of the arterial wall. Erythropoietin (EPO) is a pleiotropic cytokine released mainly by the kidneys in adults. Besides its well-known erythropoietic functions, EPO possesses anti-apoptotic, mitogenic, and angiogenic effects. This review aims to analyze the strength of any therapeutic or protective value of EPO on the heart and safety concerns regarding its administration in MI individuals. This systematic review was performed based on Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) 2020 guidelines. Four databases (PubMed, PubMed Central, Google Scholar, and Sciences Direct) were employed to search for articles published in the last 10 years. Focused studies were relevant articles in the English language, trials, reviews, meta-analyses, and studies with a control group. Following the quality assessment process, nine studies were eligible and hence were included in the review consisting of six randomized controlled trials and three systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Contrary to preclinical studies, EPO administration did not significantly have notable effects on mortality, major adverse cardiovascular events, or infarction size reduction. Significant left ventricle ejection fraction amelioration was not appreciated either. However, EPO seems to reduce the incidence of post-MI arrhythmias.
Keywords: coronary heart disease; erythropoietin; erythropoietin effects; myocardial infarction; stemi.
Copyright © 2022, Jean-Baptiste et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A small nonerythropoietic helix B surface peptide based upon erythropoietin structure is cardioprotective against ischemic myocardial damage.Mol Med. 2011 Mar-Apr;17(3-4):194-200. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2010.00235. Epub 2010 Dec 16. Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 21170473 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotics for secondary prevention of coronary heart disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Feb 23;2(2):CD003610. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003610.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33704780 Free PMC article.
-
Erythropoietin induces neovascularization and improves cardiac function in rats with heart failure after myocardial infarction.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005 Jul 5;46(1):125-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2005.03.044. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005. PMID: 15992646
-
A single dose of erythropoietin in ST-elevation myocardial infarction.Eur Heart J. 2010 Nov;31(21):2593-600. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehq304. Epub 2010 Aug 29. Eur Heart J. 2010. PMID: 20802250 Clinical Trial.
-
Cannabis use and acute coronary syndrome.Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2019 Oct;57(10):831-841. doi: 10.1080/15563650.2019.1601735. Epub 2019 Apr 9. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2019. PMID: 30964363
Cited by
-
Asialo-rhuEPO as a Potential Neuroprotectant for Ischemic Stroke Treatment.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Apr 18;16(4):610. doi: 10.3390/ph16040610. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37111367 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Underlying Cause of Death, 1999-2020. [ Feb; 2021 ];https://wonder.cdc.gov/ucd-icd10.html 2019. 2020 2021
-
- Prevalence of uncontrolled risk factors for cardiovascular disease: United States, 1999-2010. Fryar CD, Chen TC, Li X. https://books.google.ht/books?hl=en&lr=&id=MQmDxjrBdrYC&oi=fnd&pg=PA2011... NCHS Data Brief. 2012;(103):1–8. - PubMed
-
- Heart disease and stroke statistics-2021 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Virani SS, Alonso A, Aparicio HJ, et al. Circulation. 2021;143:0–743. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
