Genome-Wide Identification of PLATZ Transcription Factors in Ginkgo biloba L. and Their Expression Characteristics During Seed Development
- PMID: 35812908
- PMCID: PMC9262033
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.946194
Genome-Wide Identification of PLATZ Transcription Factors in Ginkgo biloba L. and Their Expression Characteristics During Seed Development
Abstract
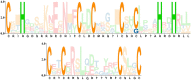
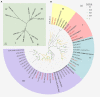
Plant AT-rich protein and zinc-binding protein (PLATZ) is a class of plant-specific zinc-dependent DNA-binding protein that binds to A/T-rich DNA sequences. PLATZ plays an important role in seed development, water tolerance, and cell proliferation in early plant growth. In this study, 11 GbPLATZs were identified from the ginkgo genome with complete PLATZ-conserved domains, which represents a smaller number compared with angiosperms. Multi-species phylogenetic analysis showed that PLATZ genes were conserved in seed plants, and the 11 members were represented by four groups, among which groups I and II were closely related. Analysis of gene structures, sequence module characteristics, and expression patterns showed that GbPLATZs were similar within and differed between groups. RNA-seq and qRT-PCR results showed that GbPLATZs had distinct expression patterns. Most genes were associated with seed development, among which six genes were highly related. Subcellular localization experiments showed that six GbPLATZ proteins related to seed development were localized in the nucleus, suggesting that they might function as traditional transcription factors. This study provides a basis for understanding the structural differentiation, evolutionary characteristics, expression profile, and potential functions of PLATZ transcription factors in Ginkgo biloba.
Keywords: Ginkgo biloba L.; PLATZ; expression pattern; seed development; subcellular localization.
Copyright © 2022 Han, Rong, Tian, Qu, Xu and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Comprehensive Genome-Wide Analysis and Expression Pattern Profiling of PLATZ Gene Family Members in Solanum Lycopersicum L. under Multiple Abiotic Stresses.Plants (Basel). 2022 Nov 15;11(22):3112. doi: 10.3390/plants11223112. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36432841 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Study of Plant-Specific PLATZ Transcription Factors and Functional Analysis of OsPLATZ1 in Regulating Caryopsis Development of Rice (Oryza sativa L.).Plants (Basel). 2025 Jan 7;14(2):151. doi: 10.3390/plants14020151. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39861505 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Characterization of PLATZ Transcription Factors in Wheat.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 25;21(23):8934. doi: 10.3390/ijms21238934. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33255649 Free PMC article.
-
PLATZ transcription factors and their emerging roles in plant responses to environmental stresses.Plant Sci. 2025 Mar;352:112400. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2025.112400. Epub 2025 Jan 27. Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 39880126 Review.
-
Ginkgo biloba seed exocarp: A waste resource with abundant active substances and other components for potential applications.Food Res Int. 2022 Oct;160:111637. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111637. Epub 2022 Jul 8. Food Res Int. 2022. PMID: 36076439 Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive Genome-Wide Analysis and Expression Pattern Profiling of PLATZ Gene Family Members in Solanum Lycopersicum L. under Multiple Abiotic Stresses.Plants (Basel). 2022 Nov 15;11(22):3112. doi: 10.3390/plants11223112. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36432841 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the PLATZ Transcription Factor in Tomato.Plants (Basel). 2023 Jul 13;12(14):2632. doi: 10.3390/plants12142632. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37514247 Free PMC article.
-
Protoplast isolation and transient transformation system for Ginkgo biloba L.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Mar 15;14:1145754. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1145754. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37063206 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of cold stress on photosynthetic physiological characteristics and molecular mechanism analysis in cold-resistant cotton (ZM36) seedlings.Front Plant Sci. 2024 May 13;15:1396666. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1396666. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38803600 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Roles of the Plant AT-Rich Sequence and Zinc-Binding (PLATZ) Gene Family in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) Under Abiotic Stresses.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 16;26(4):1682. doi: 10.3390/ijms26041682. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40004146 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Azim J. B., Khan M. F. H., Hassan L., Robin A. H. K. (2020). Genome-wide characterization and expression profiling of plant-specific PLATZ transcription factor family genes in Brassica rapa L. Plant Breed Biotechnol. 8, 28–45. doi: 10.9787/pbb.2020.8.1.28 - DOI
-
- Carneiro T., Medeiros Da Nobrega R. V., Nepomuceno T., Bian G.-B., De Albuquerque V. H. C., Reboucas Filho P. P. (2018). Performance analysis of Google Colaboratory as a tool for accelerating deep learning applications. IEEE Access 6, 61677–61685. doi: 10.1109/access.2018.2874767 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

