The miRNA-34a/Sirt1/p53 pathway in a rat model of lens regeneration
- PMID: 35813324
- PMCID: PMC9263767
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-22-2099
The miRNA-34a/Sirt1/p53 pathway in a rat model of lens regeneration
Abstract
Background: There are many molecular factors involved in Wolffian and corneal lens regeneration, but few in lens regeneration by lens epithelial cells (LECs) in mammals. Silent information regulator 1 (Sirt1) has a variety of physiological functions, such as a transport hub, and is involved in pathological conditions. We studied the expression of the microRNA (miRNA)-34a/Sirt1/tumor protein p53 (p53) pathway in a rat model of lens regeneration.
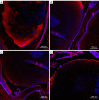
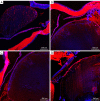
Methods: We performed extracapsular lens extraction in 42 healthy female Sprague-Dawley rats. Slit lamp observation was performed at 3, 7, 14, 21, 30, 60 and 90 days postoperatively, and the rats were killed humanely by cervical dislocation at 30, 60 and 90 days postoperatively to remove the eyeballs. We performed semiquantitative immunofluorescence analysis of Sirt1, p53, alpha-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) and fibronectin (fn), and real-time fluorescence quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) to detect the relative expressions of miRNA-34a, Sirt1, p53, aquaporin 0 (AQP 0), γA-crystallin, and beaded filament structural protein 1 (BFSP1) mRNA in the lens and posterior capsule.
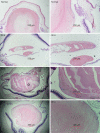
Results: The posterior capsule wrinkled at 3 days and it increased at 7 days. At 14 days, pearl-like opacification appeared under the capsule, with increasing shrinkage. Greater mass-like proliferators in size and number accumulated under the capsule and at the equator after 21 days. A regenerated lens developed in the central depression of the capsule at 30 days, slightly protruding from it. Despite being thickened at 60 days, the central depression persisted, with a smaller change at 90 days than at 60 days. Although the relative mRNA expression of miRNA-34a and p53 in the lens and posterior capsule decreased over time (P=0.000), that of Sirt1 increased (P<0.01). α-SMA was uniformly expressed in the crystals and gradually decreased, while fn expression gradually increased.
Conclusions: miRNA-34a expression decreased and Sirt1 expression increased during lens regeneration. Furthermore, p53 expression decreased, thus reducing apoptosis. Therefore, Sirt1 acted as a key factor in the pathway, and played a protective role in lens regeneration.
Keywords: Lens regeneration; miRNA-34a/Sirt1/p53 pathway; ophthalmology; rat model.
2022 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://atm.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/atm-22-2099/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Expression of transcription factors and crystallin proteins during rat lens regeneration.Mol Vis. 2010 Mar 3;16:341-52. Mol Vis. 2010. PMID: 20216939 Free PMC article.
-
[Effects of microRNA-34a on regulating silent information regulator 1 and influence of the factor on myocardial damage of rats with severe burns at early stage].Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2018 Jan 20;34(1):21-28. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-2587.2018.01.005. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29374923 Chinese.
-
miR-34a/SIRT1/p53 is suppressed by ursodeoxycholic acid in the rat liver and activated by disease severity in human non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.J Hepatol. 2013 Jan;58(1):119-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2012.08.008. Epub 2012 Aug 15. J Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 22902550
-
Expression of miR-34a in cataract rats and its related mechanism.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Feb;19(2):1051-1057. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.8295. Epub 2019 Dec 5. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32010268 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of SIRT1 and P53 in Rat Lens Epithelial cells in Experimentally Induced DM.Curr Eye Res. 2018 Apr;43(4):493-498. doi: 10.1080/02713683.2017.1410178. Epub 2017 Dec 4. Curr Eye Res. 2018. PMID: 29199862
Cited by
-
D348N Mutation of BFSP1 Gene in Congenital Cataract: it Does Matter.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2023 Dec;81(4):757-763. doi: 10.1007/s12013-023-01169-6. Epub 2023 Sep 4. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2023. PMID: 37667037
-
The sirtuin family in health and disease.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Dec 29;7(1):402. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01257-8. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 36581622 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
