The role of YKL-40 in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases: a comprehensive review
- PMID: 35813465
- PMCID: PMC9254466
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.67587
The role of YKL-40 in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases: a comprehensive review
Abstract
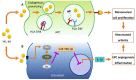
YKL-40, a chitinase-3-like protein 1 (CHI3L1) or human cartilage glycoprotein 39 (HC gp-39), is expressed and secreted by various cell-types including macrophages, chondrocytes, fibroblast-like synovial cells and vascular smooth muscle cells. Its biological function is not well elucidated, but it is speculated to have some connection with inflammatory reactions and autoimmune diseases. Although having important biological roles in autoimmunity, there were only attempts to elucidate relationships of YKL-40 with a single or couple of diseases in the literature. Therefore, in order to analyze the relationship between YKL-40 and the overall diseases, we reviewed 51 articles that discussed the association of YKL-40 with rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, systemic lupus erythematosus, Behçet disease and inflammatory bowel disease. Several studies showed that YKL-40 could be assumed as a marker for disease diagnosis, prognosis, disease activity and severity. It is also shown to be involved in response to disease treatment. However, other studies showed controversial results particularly in the case of Behçet disease activity. Therefore, further studies are needed to elucidate the exact role of YKL-40 in autoimmunity and to investigate its potential in therapeutics.
Keywords: Autoimmune disease; Biomarker; Diagnostic marker; Pathogenesis; YKL-40.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Rehli M, Krause SW, Andreesen R. Molecular characterization of the gene for human cartilage gp-39(CHI3L1), a member of the chitinase protein family and marker for late stages of macrophage differentiation. Genomics. 1997;43:221–225. - PubMed
-
- Shackelton LM, Mann DM, Millis AJ. Identification of a 38-kDa heparin-binding glycoprotein (gp38k) in differentiating vascular smooth muscle cells as a member of a group of proteins associated with tissue remodeling. J Biol Chem. 1995;270(22):13076–83. - PubMed
-
- Hakala BE, White C, Recklies AD. Human cartilage gp-39, a major secretory product of articular chondrocytes and synovial cells, is a mammalian member of a chitinase protein family. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:25803–25810. - PubMed
-
- Johansen JS, Jensen BV, Roslind A, Nielsen D, Price PA. Serum YKL-40, a new prognostic biomarker in cancer patients? Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2006;15:194–202. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

