Neuroprotective and Neurotoxic Effects of Glial-Derived Exosomes
- PMID: 35813501
- PMCID: PMC9257100
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2022.920686
Neuroprotective and Neurotoxic Effects of Glial-Derived Exosomes
Abstract
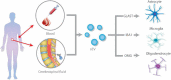
Exosomes derived from glial cells such as astrocytes, microglia, and oligodendrocytes can modulate cell communication in the brain and exert protective or neurotoxic effects on neurons, depending on the environmental context upon their release. Their isolation, characterization, and analysis under different conditions in vitro, in animal models and samples derived from patients has allowed to define the participation of other molecular mechanisms behind neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration spreading, and to propose their use as a potential diagnostic tool. Moreover, the discovery of specific molecular cargos, such as cytokines, membrane-bound and soluble proteins (neurotrophic factors, growth factors, misfolded proteins), miRNA and long-non-coding RNA, that are enriched in glial-derived exosomes with neuroprotective or damaging effects, or their inhibitors can now be tested as therapeutic tools. In this review we summarize the state of the art on how exosomes secretion by glia can affect neurons and other glia from the central nervous system in the context of neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation, but also, on how specific stress stimuli and pathological conditions can change the levels of exosome secretion and their properties.
Keywords: astrocytes; exosomes; microglia; neuroinflammation; neuroprotective; neurotoxic; oligodendrocyte.
Copyright © 2022 Oyarce, Cepeda, Lagos, Garrido, Vega-Letter, Garcia-Robles, Luz-Crawford and Elizondo-Vega.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Beneventano M., Spampinato S. F., Merlo S., Chisari M., Platania P., Ragusa M., et al. (2017). Shedding of microvesicles from microglia contributes to the effects induced by metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 activation on neuronal death. Front. Pharmacol. 8:812. 10.3389/fphar.2017.00812 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

