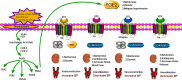
Roles of EP Receptors in the Regulation of Fluid Balance and Blood Pressure
- PMID: 35813612
- PMCID: PMC9262144
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.875425
Roles of EP Receptors in the Regulation of Fluid Balance and Blood Pressure
Abstract
Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) is an important prostanoid expressing throughout the kidney and cardiovascular system. Despite the diverse effects on fluid metabolism and blood pressure, PGE2 is implicated in sustaining volume and hemodynamics homeostasis. PGE2 works through four distinct E-prostanoid (EP) receptors which are G protein-coupled receptors. To date, pharmacological specific antagonists and agonists of all four subtypes of EP receptors and genetic targeting knockout mice for each subtype have helped in uncoupling the diverse functions of PGE2 and discriminating the respective characteristics of each receptor. In this review, we summarized the functions of individual EP receptor subtypes in the renal and blood vessels and the molecular mechanism of PGE2-induced fluid metabolism and blood pressure homeostasis.
Keywords: EP receptors; blood pressure; blood pressure (BP); fluid metabolism; hypertension; kidney; prostaglandin E2.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Wu, Jia, Yu and Huang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prostaglandin E2 receptor distribution and function in the gastrointestinal tract.Br J Pharmacol. 2006 Nov;149(6):611-23. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706923. Epub 2006 Oct 2. Br J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 17016496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distinct roles of central and peripheral prostaglandin E2 and EP subtypes in blood pressure regulation.Am J Hypertens. 2012 Oct;25(10):1042-9. doi: 10.1038/ajh.2012.67. Epub 2012 Jun 14. Am J Hypertens. 2012. PMID: 22695507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selectively targeting prostanoid E (EP) receptor-mediated cell signalling pathways: Implications for lung health and disease.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2018 Apr;49:75-87. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2018.01.008. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2018. PMID: 29408043 Review.
-
Role of EP(2) and EP(3) PGE(2) receptors in control of murine renal hemodynamics.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2001 Jan;280(1):H327-33. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.2001.280.1.H327. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11123248
-
Identification of specific EP receptors responsible for the hemodynamic effects of PGE2.Am J Physiol. 1999 Sep;277(3):H924-30. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1999.277.3.H924. Am J Physiol. 1999. PMID: 10484412
Cited by
-
Influence of sodium Bituminosulfonate and Doxycycline on signal molecules relevant for rosacea symptoms.Sci Rep. 2025 May 23;15(1):17894. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-02796-0. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40410272 Free PMC article.
-
The Link between Prostanoids and Cardiovascular Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 20;24(4):4193. doi: 10.3390/ijms24044193. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Silent Effects of High Salt: Risks Beyond Hypertension and Body's Adaptation to High Salt.Biomedicines. 2025 Mar 18;13(3):746. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13030746. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40149722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From Gut to Brain: Uncovering Potential Serum Biomarkers Connecting Inflammatory Bowel Diseases to Neurodegenerative Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 23;25(11):5676. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115676. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38891863 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of G protein coupled receptors in acute kidney injury.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Sep 2;22(1):423. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01802-8. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39223553 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources