A Case of Pulmonary Sarcoidosis during First-Line Targeted Therapy with Dabrafenib Plus Trametinib in BRAF V600E-Mutated Metastatic Melanoma
- PMID: 35813697
- PMCID: PMC9210023
- DOI: 10.1159/000524185
A Case of Pulmonary Sarcoidosis during First-Line Targeted Therapy with Dabrafenib Plus Trametinib in BRAF V600E-Mutated Metastatic Melanoma
Abstract
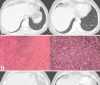
BRAF inhibitors (BRAFi) and MEK inhibitors (MEKi) exert a cytotoxic and immune-mediated effect on metastatic melanoma. The immune-mediated mechanism can lead to some adverse events, including panniculitis, erythema, keratitis, vitiligo-like lesions, or, more rarely, sarcoid-like skin reactions. In particular, sarcoidosis-related manifestations during melanoma treatment are characterized mainly by skin involvement and are seldom associated with chest or lymph node lesions. Overall, managing these adverse events can be very challenging from the diagnostic and therapeutic points of view. We present a case of pulmonary sarcoidosis; it is the first without skin involvement and initially only with lung presentation, diagnosed during treatment with BRAFi and MEKi for metastatic cutaneous melanoma. After about 2 years of treatment, with an oncological complete response, a histologically confirmed form of pulmonary sarcoidosis was diagnosed and initially interpreted as tumor progression. Sarcoidosis has always remained asymptomatic. After progression in the thorax and supraclavicular lymph nodes, steroid therapy with prednisone was instituted with total remission of the signs of disease. The targeted therapy has never been interrupted, and the patient still shows a complete response. This clinical case suggests that rare immune-mediated events, such as pulmonary sarcoidosis, should be considered during targeted therapy for metastatic melanoma and not only during treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors. It also suggests that the interruption of targeted treatment should be accurately considered based on the expected risks or benefits since such immune-mediated events may have low clinical impact.
Keywords: Dabrafenib; Immune-mediated event; Melanoma; Sarcoidosis; Targeted therapy; Trametinib.
Copyright © 2022 by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors declared conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hauschild A, Grob JJ, Demidov LV, Jouary T, Gutzmer R, Millward M, et al. Dabrafenib in BRAF-mutated metastatic melanoma: a multicentre, open-label, phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2012;380:358–65. - PubMed
-
- Dummer R, Ascierto PA, Gogas HJ, Arance A, Mandala M, Liszkay G, et al. Encorafenib plus binimetinib versus vemurafenib or encorafenib in patients with BRAF-mutant melanoma (COLUMBUS): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19((5)):603–15. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials