Effects of "Mindfulness Acceptance Insight Commitment" Training on Flow State and Mental Health of College Swimmers: A Randomized Controlled Experimental Study
- PMID: 35814092
- PMCID: PMC9263444
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.799103
Effects of "Mindfulness Acceptance Insight Commitment" Training on Flow State and Mental Health of College Swimmers: A Randomized Controlled Experimental Study
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Effects of "mindfulness acceptance insight commitment" training on flow state and mental health of college swimmers: a randomized controlled experimental study.Front Psychol. 2024 Jan 18;15:1369142. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1369142. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 38304919 Free PMC article.
Abstract
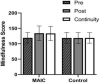
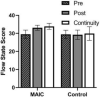
This research explores the intervention effect of the mindfulness acceptance insight commitment (MAIC) training program on the mindfulness level, flow state, and mental health of college swimmers. A sample of 47 college swimmers from a regular university was recruited and randomly divided into two groups before the intervention. Independent variables between groups are psychological training mode (MAIC training/no training), and the independent variable within group was time (pre-test, post-test, and continuity test). The dependent variables are mindfulness level, flow state, and mental health (anxiety, depression, training, and competition satisfaction). Results show that after the intervention of MAIC training, the mindfulness level of athletes' flow state has been significantly improved, whereas anxiety and depression significantly decreased. In addition, the satisfaction with training and competition significantly improved. In the continuous stage after the intervention, the mindfulness level, flow state, and mental health of athletes are still significantly higher than those in the pre-test. The comparison of the post-test and continuity test show no significant differences in the mindfulness level, flow state, depression, and training and competition satisfaction of athletes. Still, the anxiety level shows an upward trend with a significant difference. This study demonstrates that the MAIC mindfulness training program can significantly improve the mindfulness level, flow state, anxiety, depression, and training and competition satisfaction of college swimmers with a good continuity effect. Thus, the athletes' sports experience can be improved, and good psychological benefits can be attained.
Keywords: college swimmers; flow state; mental health; mindfulness training; randomized controlled trial.
Copyright © 2022 Ning, Hao and Huang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

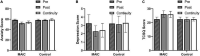
Similar articles
-
Mindfulness and acceptance-based training for elite adolescent athletes: a mixed-method exploratory study.Front Psychol. 2024 May 27;15:1401763. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1401763. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 38860040 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of mindfulness intervention on competition state anxiety in sprinters-a randomized controlled trial.Front Psychol. 2024 Oct 31;15:1418094. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1418094. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39545139 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of mindfulness training on the psychological state of high-level athletes: Meta analysis and system evaluation research.J Sports Sci. 2025 Mar;43(6):600-622. doi: 10.1080/02640414.2025.2468997. Epub 2025 Feb 26. J Sports Sci. 2025. PMID: 40010739
-
Exploring mindfulness interventions across cultures: a comparative meta-analysis of mindfulness interventions for athletes in Western and Eastern contexts.Front Psychol. 2024 Oct 31;15:1449886. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1449886. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39545142 Free PMC article.
-
A meta-analysis of the intervention effect of mindfulness training on athletes' performance.Front Psychol. 2024 May 31;15:1375608. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1375608. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 38939219 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Effect of Mindfulness Intervention on the Psychological Skills and Shooting Performances in Male Collegiate Basketball Athletes in Macau: A Quasi-Experimental Study.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Jan 28;20(3):2339. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20032339. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36767706 Free PMC article.
-
Variables e instrumentos para evaluar la salud mental en nadadores de competición: una revisión narrativa.F1000Res. 2024 Apr 18;12:1281. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.140504.3. eCollection 2023. F1000Res. 2024. PMID: 38799244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessing Decentering Capacity in Athletes: A Moderated Mediation Model.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Feb 14;20(4):3324. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20043324. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36834019 Free PMC article.
-
How flow and mindfulness interact with each other in mindfulness-based augmented reality mandala coloring activities.Front Psychol. 2024 Jan 8;14:1301531. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1301531. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 38259530 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Yoga on Athletes' Mental Well-Being: An Experimental Study.Cureus. 2024 Aug 2;16(8):e66044. doi: 10.7759/cureus.66044. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39224730 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beili Z. (1993). Revision of Chinese norm of sports competition anxiety scale. Psychol. Sci. 16:6.
-
- Beili Z. (1995). Brief introduction of POMS scale and and its model for China. J Tianjin Instit. Phys. Educ. 1 35–7.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

