Role of microRNA/lncRNA Intertwined With the Wnt/β-Catenin Axis in Regulating the Pathogenesis of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- PMID: 35814205
- PMCID: PMC9263262
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.814971
Role of microRNA/lncRNA Intertwined With the Wnt/β-Catenin Axis in Regulating the Pathogenesis of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Abstract
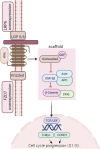
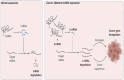
Objective (s): In this mini-review, we aimed to discuss the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway modulation in triple-negative breast cancer, particularly the contribution of lncRNAs and miRNAs in its regulation and their possible entwining role in breast cancer pathogenesis, proliferation, migration, or malignancy. Background: Malignant tumor formation is very high for breast cancer in women and is a leading cause of death all over the globe. Among breast cancer subtypes, triple-negative breast cancer is rife in premenopausal women, most invasive, and prone to metastasis. Complex pathways are involved in this cancer's pathogenesis, advancement, and malignancy, including the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. This pathway is conserved among vertebrates and is necessary for sustaining cell homeostasis. It is regulated by several elements such as transcription factors, enhancers, non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs and miRNAs), etc. Methods: We evaluated lncRNAs and miRNAs differentially expressed in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) from the cDNA microarray data set literature survey. Using in silico analyses combined with a review of the current literature, we anticipated identifying lncRNAs and miRNAs that might modulate the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Result: The miRNAs and lncRNAs specific to triple-negative breast cancer have been identified based on literature and database searches. Tumorigenesis, metastasis, and EMT were all given special attention. Apart from cross-talk being essential for TNBC tumorigenesis and treatment outcomes, our results indicated eight upregulated and seven downregulated miRNAs and 19 upregulated and three downregulated lncRNAs that can be used as predictive or diagnostic markers. This consolidated information could be useful in the clinic and provide a combined literature resource for TNBC researchers working on the Wnt/β-catenin miRNA/lncRNA axis. Conclusion: In conclusion, because the Wnt pathway and miRNAs/lncRNAs can modulate TNBC, their intertwinement results in a cascade of complex reactions that affect TNBC and related processes. Their function in TNBC pathogenesis has been highlighted in molecular processes underlying the disease progression.
Keywords: breast cancer; lncRNA; microRNA; pathogenesis; wnt/β-catenin.
Copyright © 2022 Hu, Zhang, Xing and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Coordinated regulation of WNT/β-catenin, c-Met, and integrin signalling pathways by miR-193b controls triple negative breast cancer metastatic traits.BMC Cancer. 2021 Dec 4;21(1):1296. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08955-6. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34863149 Free PMC article.
-
Kinesin family member 23, regulated by FOXM1, promotes triple negative breast cancer progression via activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022 May 7;41(1):168. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02373-7. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35524313 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA DGCR5 incudes tumorigenesis of triple-negative breast cancer by affecting Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.J BUON. 2020 Mar-Apr;25(2):702-708. J BUON. 2020. PMID: 32521856
-
The functional significance and cross-talk of non-coding RNAs in triple negative and quadruple negative breast cancer.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Jul;49(7):6899-6918. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07288-2. Epub 2022 Mar 2. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35235157 Review.
-
Countering Triple Negative Breast Cancer via Impeding Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling, a Phytotherapeutic Approach.Plants (Basel). 2022 Aug 24;11(17):2191. doi: 10.3390/plants11172191. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36079579 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deciphering the code: the pivotal role of lncRNAs in advancing TNBC therapy.Front Oncol. 2024 Sep 2;14:1450980. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1450980. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39286016 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The current landscape of the antimicrobial peptide melittin and its therapeutic potential.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 22;15:1326033. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1326033. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38318188 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long non-coding RNAs PTENP1, GNG12-AS1, MAGI2-AS3 and MEG3 as tumor suppressors in breast cancer and their associations with clinicopathological parameters.Cancer Biomark. 2024;40(1):61-78. doi: 10.3233/CBM-230259. Cancer Biomark. 2024. PMID: 38277283 Free PMC article.
-
Expression pattern, prognostic value and potential microRNA silencing of FZD8 in breast cancer.Oncol Lett. 2023 Sep 21;26(5):477. doi: 10.3892/ol.2023.14065. eCollection 2023 Nov. Oncol Lett. 2023. PMID: 37809047 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding Breast Cancer: Awareness, Risk Factors, and Symptoms Among Female Health Science Students in Hungary.Healthcare (Basel). 2025 Jun 25;13(13):1512. doi: 10.3390/healthcare13131512. Healthcare (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40648537 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agustsson A. S., Birgisson H., Agnarsson B. A., Jonsson T., Stefansdottir H., Wärnberg F., et al. (2020). In Situ breast Cancer Incidence Patterns in Iceland and Differences in Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Treatment Compared to Sweden. Sci. Rep. 10 (1), 17623. 10.1038/s41598-020-74134-5 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources