Profiling COVID-19 Vaccine Adverse Events by Statistical and Ontological Analysis of VAERS Case Reports
- PMID: 35814246
- PMCID: PMC9263450
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.870599
Profiling COVID-19 Vaccine Adverse Events by Statistical and Ontological Analysis of VAERS Case Reports
Abstract
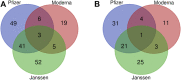
Since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, vaccines have been developed to mitigate the spread of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. These vaccines have been effective in reducing the rate and severity of COVID-19 infection but also have been associated with various adverse events (AEs). In this study, data from the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) was queried and analyzed via the Cov19VaxKB vaccine safety statistical analysis tool to identify statistically significant (i.e., enriched) AEs for the three currently FDA-authorized or approved COVID-19 vaccines. An ontology-based classification and literature review were conducted for these enriched AEs. Using VAERS data as of 31 December 2021, 96 AEs were found to be statistically significantly associated with the Pfizer-BioNTech, Moderna, and/or Janssen COVID-19 vaccines. The Janssen COVID-19 vaccine had a higher crude reporting rate of AEs compared to the Moderna and Pfizer COVID-19 vaccines. Females appeared to have a higher case report frequency for top adverse events compared to males. Using the Ontology of Adverse Event (OAE), these 96 adverse events were classified to different categories such as behavioral and neurological AEs, cardiovascular AEs, female reproductive system AEs, and immune system AEs. Further statistical comparison between different ages, doses, and sexes was also performed for three notable AEs: myocarditis, GBS, and thrombosis. The Pfizer vaccine was found to have a closer association with myocarditis than the other two COVID-19 vaccines in VAERS, while the Janssen vaccine was more likely to be associated with thrombosis and GBS AEs. To support standard AE representation and study, we have also modeled and classified the newly identified thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome (TTS) AE and its subclasses in the OAE by incorporating the Brighton Collaboration definition. Notably, severe COVID-19 vaccine AEs (including myocarditis, GBS, and TTS) rarely occur in comparison to the large number of COVID-19 vaccinations administered in the United States, affirming the overall safety of these COVID-19 vaccines.
Keywords: COVID-19; COVID-19 vaccine; Cov19VaxKB; SARS-CoV-2; VAERS; adverse events; ontology; ontology of adverse events.
Copyright © 2022 Guo, Deguise, Tian, Huang, Goru, Yang, Peng, Zhang, Zhao, Xie and He.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Determinants of COVID-19 vaccine-induced myocarditis.Ther Adv Drug Saf. 2024 Jan 27;15:20420986241226566. doi: 10.1177/20420986241226566. eCollection 2024. Ther Adv Drug Saf. 2024. PMID: 38293564 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics and Comparison of Adverse Events of Coronavirus Disease 2019 Vaccines Reported to the United States Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System Between 14 December 2020 and 8 October 2021.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Apr 5;9:826327. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.826327. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35449806 Free PMC article.
-
Use of COVID-19 Vaccines After Reports of Adverse Events Among Adult Recipients of Janssen (Johnson & Johnson) and mRNA COVID-19 Vaccines (Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna): Update from the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices - United States, July 2021.MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021 Aug 13;70(32):1094-1099. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7032e4. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021. PMID: 34383735 Free PMC article.
-
Post-authorization safety surveillance of Ad.26.COV2.S vaccine: Reports to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System and v-safe, February 2021-February 2022.Vaccine. 2023 Jul 5;41(30):4422-4430. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2023.06.023. Epub 2023 Jun 14. Vaccine. 2023. PMID: 37321898 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 vaccines: comparison of biological, pharmacological characteristics and adverse effects of Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna Vaccines.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021 Feb;25(3):1663-1669. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202102_24877. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33629336 Review.
Cited by
-
Hearing Loss after COVID-19 and Non-COVID-19 Vaccination: A Systematic Review.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Dec 9;11(12):1834. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11121834. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38140238 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Different Types of COVID-19 Vaccines on Menstrual Cycles of Females of Reproductive Age Group (15-49): A Multinational Cross-Sectional Study.Cureus. 2023 May 29;15(5):e39640. doi: 10.7759/cureus.39640. eCollection 2023 May. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37388582 Free PMC article.
-
B-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma following intravenous BNT162b2 mRNA booster in a BALB/c mouse: A case report.Front Oncol. 2023 May 1;13:1158124. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1158124. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37197431 Free PMC article.
-
The Ambivalence of Post COVID-19 Vaccination Responses in Humans.Biomolecules. 2024 Oct 17;14(10):1320. doi: 10.3390/biom14101320. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39456253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune response against viral infections and nucleic acid-based vaccines.Scand J Immunol. 2022 Dec;96(6):e13221. doi: 10.1111/sji.13221. Epub 2022 Oct 13. Scand J Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36300515 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ashorobi D., Ameer M. A., Fernandez R. (2022). “Thrombosis,” in StatPearls (Treasure Island FL. - PubMed
-
- Brighton Collaboration (2021). Interim Case Definition of Thrombosis with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome (TTS). [Online]. Available: https://brightoncollaboration.us/thrombosis-with-thrombocytopenia-syndro... .
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

