Bioinformatics Analysis of miRNAs and mRNAs Network-Xuefu Zhuyu Decoction Exerts Neuroprotection of Traumatic Brain Injury Mice in the Subacute Phase
- PMID: 35814248
- PMCID: PMC9257413
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.772680
Bioinformatics Analysis of miRNAs and mRNAs Network-Xuefu Zhuyu Decoction Exerts Neuroprotection of Traumatic Brain Injury Mice in the Subacute Phase
Abstract
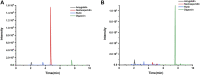
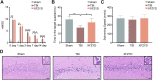
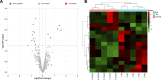
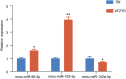
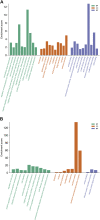
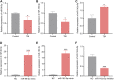
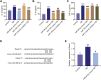
Xuefu Zhuyu decoction (XFZYD) is used to treat traumatic brain injury (TBI). XFZYD-based therapies have achieved good clinical outcomes in TBI. However, the underlying mechanisms of XFZYD in TBI remedy remains unclear. The study aimed to identify critical miRNAs and putative mechanisms associated with XFYZD through comprehensive bioinformatics analysis. We established a controlled cortical impact (CCI) mice model and treated the mice with XFZYD. The high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS) confirmed the quality of XFZYD. The modified neurological severity score (mNSS) and Morris water maze (MWM) tests indicated that XFZYD improved the neurological deficit (p < 0.05) and cognitive function (p < 0.01). Histological analysis validated the establishment of the CCI model and the treatment effect of XFZYD. HE staining displayed that the pathological degree in the XFZYD-treated group was prominently reduced. The transcriptomic data was generated using microRNA sequencing (miRNA-seq) of the hippocampus. According to cluster analysis, the TBI group clustered together was distinct from the XFZYD group. Sixteen differentially expressed (5 upregulated; 11 downregulated) miRNAs were detected between TBI and XFZYD. The reliability of the sequencing data was confirmed by qRT-PCR. Three miRNAs (mmu-miR-142a-5p, mmu-miR-183-5p, mmu-miR-96-5p) were distinctively expressed in the XFZYD compared with the TBI and consisted of the sequencing results. Bioinformatics analysis suggested that the MAPK signaling pathway contributes to TBI pathophysiology and XFZYD treatment. Subsequently, the functions of miR-96-5p, miR-183-5p, and miR-142a-5p were validated in vitro. TBI significantly induces the down-expression of miR-96-5p, and up-expression of inflammatory cytokines, which were all inhibited by miR-96-5p mimics. The present research provides an adequate fundament for further knowing the pathologic and prognostic process of TBI and supplies deep insights into the therapeutic effects of XFZYD.
Keywords: Bioinformatic analysis; MicroRNAs; neurological recovery; traumatic brain injury; xuefu zhuyu decoction.
Copyright © 2022 Yang, Wu, Li, Tang, Wang, Huang and Fan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Systematic analysis of tRNA-derived small RNAs reveals therapeutic targets of Xuefu Zhuyu decoction in the cortexes of experimental traumatic brain injury.Phytomedicine. 2022 Jul 20;102:154168. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154168. Epub 2022 May 14. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 35623157
-
Xuefu Zhuyu decoction promotes synaptic plasticity by targeting miR-191a-5p/BDNF-TrkB axis in severe traumatic brain injury.Phytomedicine. 2024 Jul;129:155566. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155566. Epub 2024 Mar 23. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38565001
-
TMT-based proteomics analysis reveals the protective effects of Xuefu Zhuyu decoction in a rat model of traumatic brain injury.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Aug 10;258:112826. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112826. Epub 2020 Apr 13. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32298754
-
A Chinese classical prescription Xuefu Zhuyu decoction in the treatment of coronary heart disease: An overview.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 4;10(7):e28919. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28919. eCollection 2024 Apr 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38617912 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The efficacy and safety of Xuefu Zhuyu Decoction combined with Mifepristone in the treatment of uterine leiomyoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Dec 5;281:114551. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114551. Epub 2021 Aug 21. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34428523
Cited by
-
Metabolomics integrated with network pharmacology of blood-entry constituents reveals the bioactive component of Xuefu Zhuyu decoction and its angiogenic effects in treating traumatic brain injury.Chin Med. 2024 Sep 26;19(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s13020-024-01001-0. Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 39327620 Free PMC article.
-
Tailoring a traditional Chinese medicine prescription for complex diseases: A novel multi-targets-directed gradient weighting strategy.J Pharm Anal. 2025 Apr;15(4):101199. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2025.101199. Epub 2025 Jan 16. J Pharm Anal. 2025. PMID: 40297631 Free PMC article.
-
A Direct Relationship Between 'Blood Stasis' and Fibrinaloid Microclots in Chronic, Inflammatory, and Vascular Diseases, and Some Traditional Natural Products Approaches to Treatment.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 May 12;18(5):712. doi: 10.3390/ph18050712. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40430532 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

