Yu-Ping-Feng Formula Ameliorates Alveolar-Capillary Barrier Injury Induced by Exhausted-Exercise via Regulation of Cytoskeleton
- PMID: 35814249
- PMCID: PMC9263595
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.891802
Yu-Ping-Feng Formula Ameliorates Alveolar-Capillary Barrier Injury Induced by Exhausted-Exercise via Regulation of Cytoskeleton
Abstract
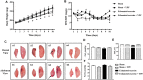
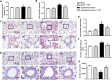
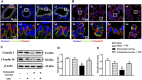
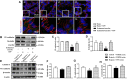
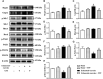
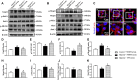
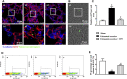
Background: Yu-ping-feng powder (YPF) is a compound traditional Chinese medicine extensively used in China for respiratory diseases. However, the role of YPF in alveolar-capillary barrier dysfunction remains unknown. This study aimed to explore the effect and potential mechanism of YPF on alveolar-capillary barrier injury induced by exhausted exercise. Methods: Male Sprague-Dawley rats were used to establish an exhausted-exercise model by using a motorized rodent treadmill. YPF at doses of 2.18 g/kg was administrated by gavage before exercise training for 10 consecutive days. Food intake-weight/body weight, blood gas analysis, lung water percent content, BALF protein concentration, morphological observation, quantitative proteomics, real-time PCR, and Western blot were performed. A rat pulmonary microvascular endothelial cell line (PMVEC) subjected to hypoxia was applied for assessing the related mechanism. Results: YPF attenuated the decrease of food intake weight/body weight, improved lung swelling and hemorrhage, alleviated the increase of lung water percent content and BALF protein concentration, and inhibited the impairment of lung morphology. In addition, YPF increased the expression of claudin 3, claudin 18, occludin, VE-cadherin, and β-catenin, attenuated the epithelial and endothelial hyperpermeability in vivo and/or in vitro, and the stress fiber formation in PMVECs after hypoxia. Quantitative proteomics discovered that the effect of YPF implicated the Siah2-ubiquitin-proteasomal pathway, Gng12-PAK1-MLCK, and RhoA/ROCK, which was further confirmed by Western blot. Data are available via ProteomeXchange with identifier PXD032737. Conclusion: YPF ameliorated alveolar-capillary barrier injury induced by exhausted exercise, which is accounted for at least partly by the regulation of cytoskeleton.
Keywords: cell junctions; lung injury; proteomics; stress fiber; traditional Chinese medicine.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Li, Pan, Yan, Sun, Wang, Anwaier, Liao, Xie, Fan, Huo, Wang and Han.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Yu-Ping-Feng Formula Exerts Antilung Cancer Effects by Remodeling the Tumor Microenvironment through Regulating Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Apr 20;2021:6624461. doi: 10.1155/2021/6624461. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 33986819 Free PMC article.
-
Preventive effects of a fractioned polysaccharide from a traditional Chinese herbal medical formula (Yu Ping Feng San) on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic fibrosis.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2010 Jul;62(7):935-42. doi: 10.1211/jpp.62.07.0016. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20636883
-
Analysis of immunostimulatory activity of polysaccharide extracted from Yu-Ping-Feng in vitro and in vivo.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Sep;93:146-155. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.05.138. Epub 2017 Jun 17. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28628831
-
Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic evaluation of the major component astragaloside IV on the immunomodulatory effects of Yu-ping-feng prescription.Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2014 Jun;39(2):103-10. doi: 10.1007/s13318-013-0161-x. Epub 2013 Dec 18. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2014. PMID: 24346849
-
Effects of Yu-Ping-Feng polysaccharides on animal growth performance and immune function: a review.Front Vet Sci. 2023 Sep 20;10:1260208. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1260208. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 37799408 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Yupingfeng Polysaccharides as Feed Supplement on Immune Function and Intestinal Microbiome in Chickens.Microorganisms. 2023 Nov 15;11(11):2774. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11112774. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 38004785 Free PMC article.
-
Adjuvant treatment with yupingfeng granules for recurrent respiratory tract infections in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Pediatr. 2022 Dec 21;10:1005745. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.1005745. eCollection 2022. Front Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 36619520 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An updated meta-analysis of Chinese herbal medicine for the prevention of COVID-19 based on Western-Eastern medicine.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Nov 13;14:1257345. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1257345. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 38044944 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asano T., Morishita R., Ueda H., Asano M., Kato K. (1998). GTP-Binding Protein Gamma12 Subunit Phosphorylation by Protein Kinase C-Iidentification of the Phosphorylation Site and Factors Involved in Cultured Cells and Rat Tissues In Vivo . Eur. J. Biochem. 251 (1-2), 314–319. 10.1046/j.1432-1327.1998.2510314.x - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

