circ_0072464 Shuttled by Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Secreted Extracellular Vesicles Inhibits Nucleus Pulposus Cell Ferroptosis to Relieve Intervertebral Disc Degeneration
- PMID: 35814268
- PMCID: PMC9259290
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/2948090
circ_0072464 Shuttled by Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Secreted Extracellular Vesicles Inhibits Nucleus Pulposus Cell Ferroptosis to Relieve Intervertebral Disc Degeneration
Abstract
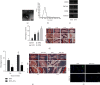
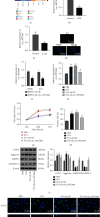
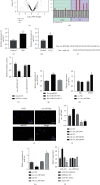
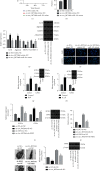
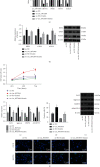
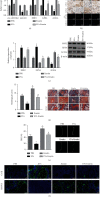
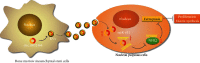
Ferroptosis, as an iron-dependent form of necrotic cell death, has been reported to affect activities of nucleus pulposus cells (NPCs). However, its role in the pathogenesis of intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD) is largely unknown. Notably, our bioinformatics analysis predicted that circ_0072464 was downregulated in nucleus pulposus of IDD mice. Therefore, this study is aimed at clarifying the mechanisms of extracellular vesicle- (EV-) encapsulated circ_0072464 derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) in NPC ferroptosis in IDD. EVs were extracted from mouse BMSCs (BMSC-EVs) and then cocultured with IL-1β-induced NPCs, followed by detection of matrix synthesis, proliferation, and ferroptosis of NPCs based on gain- or loss-of-function experiments. It was found that the uptake of BMSC-EVs by NPCs alleviated IDD. circ_0072464 and NRF2 were downregulated, and miR-431 was upregulated in IDD. Mechanistically, circ_0072464 competitively bound to miR-431, which targeted and inhibited NRF2 expression. BMSC-derived EVs carrying circ_0072464 inhibited NPC ferroptosis to promote matrix synthesis and proliferation of NPCs by inhibiting miR-431 and upregulating NRF2. Besides, in vivo experiments also confirmed that BMSC-EVs alleviated intervertebral disc lesions in mice with IDD through the circ_0072464/miR-431/NRF2 axis. Collectively, BMSC-EV-loaded circ_0072464 inhibited NPC ferroptosis to relieve IDD via upregulation of miR-431-mediated NRF2, therefore providing a potential therapeutic target against IDD.
Copyright © 2022 Xiaojun Yu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Carrying circ_0050205 Attenuate Intervertebral Disc Degeneration.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Jul 5;2022:8983667. doi: 10.1155/2022/8983667. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35847582 Free PMC article.
-
Bone mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles promote the repair of intervertebral disc degeneration by transferring microRNA-199a.Cell Cycle. 2021 Feb;20(3):256-270. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2020.1863682. Epub 2021 Jan 26. Cell Cycle. 2021. PMID: 33499725 Free PMC article.
-
Small extracellular vesicles from hypoxic mesenchymal stem cells alleviate intervertebral disc degeneration by delivering miR-17-5p.Acta Biomater. 2022 Mar 1;140:641-658. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2021.11.044. Epub 2021 Dec 5. Acta Biomater. 2022. PMID: 34879291
-
[Mechanism of extracellular vesicles in the repair of intervertebral disc degeneration].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2025 Apr 25;42(2):409-416. doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.202403046. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40288986 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
The Mechanism and Function of miRNA in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration.Orthop Surg. 2022 Mar;14(3):463-471. doi: 10.1111/os.13204. Epub 2022 Feb 9. Orthop Surg. 2022. PMID: 35142050 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting Ferroptosis Holds Potential for Intervertebral Disc Degeneration Therapy.Cells. 2022 Nov 5;11(21):3508. doi: 10.3390/cells11213508. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36359904 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of ferroptosis in intervertebral disc degeneration.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Jul 27;11:1219840. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1219840. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37576601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Potential Roles of Ferroptosis in Pathophysiology and Treatment of Musculoskeletal Diseases-Opportunities, Challenges, and Perspectives.J Clin Med. 2023 Mar 8;12(6):2125. doi: 10.3390/jcm12062125. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36983130 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of the Nrf2/HO-1 axis by mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles: implications for disease treatment.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Jun 10;12:1397954. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1397954. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38915448 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PDE4B promotes ferroptosis in nucleus pulposus cells and is involved in intervertebral disc degeneration.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 1;15(1):3984. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-87639-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39893206 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lu S., Song Y., Luo R., et al. Ferroportin-dependent iron homeostasis protects against oxidative stress-induced nucleus pulposus cell ferroptosis and ameliorates intervertebral disc degeneration in vivo. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity . 2021;2021:18. doi: 10.1155/2021/6670497.6670497 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

