The Role of Tumor Microenvironment in Invasion and Metastasis of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 35814365
- PMCID: PMC9257257
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.911285
The Role of Tumor Microenvironment in Invasion and Metastasis of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
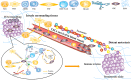
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is one of the most common cancers in the world, with a high rate of morbidity. The invasion and metastasis of ESCC is the main reason for high mortality. More and more evidence suggests that metastasized cancer cells require cellular elements that contribute to ESCC tumor microenvironment (TME) formation. TME contains many immune cells and stromal components, which are critical to epithelial-mesenchymal transition, immune escape, angiogenesis/lymphangiogenesis, metastasis niche formation, and invasion/metastasis. In this review, we will focus on the mechanism of different microenvironment cellular elements in ESCC invasion and metastasis and discuss recent therapeutic attempts to restore the tumor-suppressing function of cells within the TME. It will represent the whole picture of TME in the metastasis and invasion process of ESCC.
Keywords: esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; immune regulation; invasion; metastasis; tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2022 Zheng, Liu and Guan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Roles of circRNA dysregulation in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma tumor microenvironment.Front Oncol. 2023 Jun 13;13:1153207. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1153207. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37384299 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and characterization of prognosis-related genes in the tumor microenvironment of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Jul;96:107616. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107616. Epub 2021 May 28. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34162127
-
Long noncoding RNA RP11-766N7.4 functions as a tumor suppressor by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Apr;88:778-785. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.01.124. Epub 2017 Jan 31. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28157654
-
MiR-424-5p participates in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma invasion and metastasis via SMAD7 pathway mediated EMT.Diagn Pathol. 2016 Sep 15;11(1):88. doi: 10.1186/s13000-016-0536-9. Diagn Pathol. 2016. PMID: 27628042 Free PMC article.
-
Immune evasion in esophageal squamous cell cancer: From the perspective of tumor microenvironment.Front Oncol. 2023 Jan 9;12:1096717. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1096717. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36698392 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
LINC00330/CCL2 axis-mediated ESCC TAM reprogramming affects tumor progression.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024 May 20;29(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s11658-024-00592-8. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024. PMID: 38769475 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic treatments for resectable carcinoma of the esophagus.World J Gastroenterol. 2023 Aug 14;29(30):4628-4641. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i30.4628. World J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37662861 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling Another Dimension: Advanced Visualization of Cancer Invasion and Metastasis via Micro-CT Imaging.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Mar 28;17(7):1139. doi: 10.3390/cancers17071139. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40227647 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs: A novel signature in the metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Mar 21;30(11):1497-1523. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i11.1497. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38617454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lymphatic endothelial cell-mediated accumulation of CD177+Treg cells suppresses antitumor immunity in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Oncoimmunology. 2024 Mar 20;13(1):2327692. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2024.2327692. eCollection 2024. Oncoimmunology. 2024. PMID: 38516269 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

