Highly Synergistic Effects of Melittin With Vancomycin and Rifampin Against Vancomycin and Rifampin Resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis
- PMID: 35814659
- PMCID: PMC9260053
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.869650
Highly Synergistic Effects of Melittin With Vancomycin and Rifampin Against Vancomycin and Rifampin Resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis
Abstract
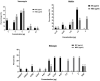
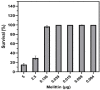
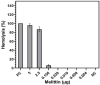
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis (MRSE) strains are increasingly emerging as serious pathogens because they can be resistant to many antibiotics called multidrug resistance (MDR) that limit the therapeutic options. In the case of vancomycin- and rifampin-resistant MDR-MRSE, the physicians are not allowed to increase the doses of antibiotics because of severe toxicity. Accordingly, we investigated the synergistic activity of melittin antimicrobial peptide with vancomycin and rifampin against vancomycin-resistant, and rifampin-resistant MDR-MRSE isolates. Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC), minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC), fractional inhibitory concentration index (FICi), and fractional bactericidal concentration index (FBCi) of antimicrobial agents against isolates were determined. Coagulate activities and serum and salt stability as well as melittin cytotoxicity on the human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293 cells and human red blood cells (RBCs) at their synergistic concentrations. MIC and MBC values for melittin were in the range of 0.312-2.5 and 0.312-5, respectively. Results also showed that the interaction of melittin with drugs was highly synergistic in which the geometric means of FICi and FBCi were < 0.5. Induced synergism led to a decrease in melittin, rifampin, and vancomycin concentrations by 8-1,020, 2-16, and 4-16-folds, respectively. This phenomenon caused a reduction in melittin toxicity by which the synergistic concentration of melittin needed to kill bacteria did not show cytotoxicity and hemolytic activity. Besides, no coagulation activity was found for the synergistic and alone concentrations of melittin in both Prothrombin Time (PT) and Partial Thromboplastin Time (PTT). Interestingly, the antibacterial activity of melittin in Mueller Hinton Broth (MHB) containing human serum did no significant differences between MIC and MBC values of melittin in MHB and MHB containing 10% human serum. The present findings showed that the therapeutic index of melittin was improved by 32.08- and 12.82-folds when combined with vancomycin and rifampin, respectively. Taken together, the obtained data show that melittin alone was effective against MDR-MRSE isolates and this antimicrobial peptide showed highly synergistic effects with vancomycin and rifampin without causing toxicity. Therefore, the combination of melittin and traditional antibiotics could be a promising strategy for the treatment of infections caused by MDR-MRSE.
Keywords: MDR; MRSE; melittin; rifampin-resistant; synergism; vancomycin-resistant.
Copyright © 2022 Mirzaei, Alikhani, Arciola, Sedighi, Irajian, Jamasbi, Yousefimashouf and Bagheri.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The issue beyond resistance: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm formation is induced by subinhibitory concentrations of cloxacillin, cefazolin, and clindamycin.PLoS One. 2022 Nov 9;17(11):e0277287. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0277287. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36350834 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiofilm effect of melittin alone and in combination with conventional antibiotics toward strong biofilm of MDR-MRSA and -Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Front Microbiol. 2023 Feb 20;14:1030401. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1030401. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36910230 Free PMC article.
-
Prevention, inhibition, and degradation effects of melittin alone and in combination with vancomycin and rifampin against strong biofilm producer strains of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Mar;147:112670. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112670. Epub 2022 Feb 3. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 35123230
-
A hope for ineffective antibiotics to return to treatment: investigating the anti-biofilm potential of melittin alone and in combination with penicillin and oxacillin against multidrug resistant-MRSA and -VRSA.Front Microbiol. 2024 Feb 1;14:1269392. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1269392. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38370578 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic Effect of Colistin and Rifampin Against Multidrug Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Open Microbiol J. 2017 Apr 28;11:63-71. doi: 10.2174/1874285801711010063. eCollection 2017. Open Microbiol J. 2017. PMID: 28553417 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The issue beyond resistance: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm formation is induced by subinhibitory concentrations of cloxacillin, cefazolin, and clindamycin.PLoS One. 2022 Nov 9;17(11):e0277287. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0277287. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36350834 Free PMC article.
-
The Opportunistic Pathogen Staphylococcus warneri: Virulence and Antibiotic Resistance, Clinical Features, Association with Orthopedic Implants and Other Medical Devices, and a Glance at Industrial Applications.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Oct 15;13(10):972. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13100972. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39452238 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vitro and in vivo anti-Pseudomonas aeruginosa activity of a scorpion peptide derivative.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jul 1;16:1622282. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1622282. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40666802 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiofilm effect of melittin alone and in combination with conventional antibiotics toward strong biofilm of MDR-MRSA and -Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Front Microbiol. 2023 Feb 20;14:1030401. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1030401. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36910230 Free PMC article.
-
The Combination of Antibiotic and Non-Antibiotic Compounds Improves Antibiotic Efficacy against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 23;24(20):15493. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015493. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37895172 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aghazadeh H., Memariani H., Ranjbar R., Pooshang Bagheri K. (2019). The activity and action mechanism of novel short selective LL-37-derived anticancer peptides against clinical isolates of Escherichia coli. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 93 75–83. - PubMed
-
- Akbari R., Hakemi-Vala M., Pashaie F., Bevalian P., Hashemi A., Pooshang Bagheri K. (2019). Highly synergistic effects of melittin with conventional antibiotics against multidrug-resistant isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microb. Drug Resist. 25 193–202. - PubMed
-
- Arciola C. R., Campoccia D., Baldassarri L., Donati M. E., Pirini V., Gamberini S., et al. (2006). Detection of biofilm formation in Staphylococcus epidermidis from implant infections. Comparison of a PCR-method that recognizes the presence of ica genes with two classic phenotypic methods. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 76 425–430. 10.1002/jbm.a.30552 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

