IS 6110 Copy Number in Multi-Host Mycobacterium bovis Strains Circulating in Bovine Tuberculosis Endemic French Regions
- PMID: 35814675
- PMCID: PMC9260277
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.891902
IS 6110 Copy Number in Multi-Host Mycobacterium bovis Strains Circulating in Bovine Tuberculosis Endemic French Regions
Abstract
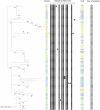
IS6110 is an insertion sequence found in the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex, to which Mycobacterium bovis belongs, which can play a role in genome plasticity and in bacterial evolution. In this study, the abundance and location of IS6110 on M. bovis genomic data of French animal field strains were studied. A first analysis was performed on a panel of 81 strains that reflect the national M. bovis population's genetic diversity. The results show that more than one-third of them are IS6110 multicopy and that 10% have IS6110 in a high copy number (more than 6 copies). Multicopy strains are those circulating in the regions where prevalence was above the national average. Further study of 93 such strains, with an IS6110 copy number of 10-12, showed stability of IS6110 copy number and genome location over time and between host species. The correlation between M. bovis multicopy strains and high bovine tuberculosis (bTB) prevalence leads us to consider whether their epidemiological success could be partly due to genetic changes originated by IS6110 transposition.
Keywords: France; IS6110; Mycobacterium bovis; bovine tuberculosis (bTB); insertion sequence (IS).
Copyright © 2022 Charles, Conde, Biet, Boschiroli and Michelet.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of an IS6110 insertion site in plcD, the unique phospholipase C gene of Mycobacterium bovis.J Med Microbiol. 2006 Apr;55(Pt 4):451-457. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.46364-0. J Med Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16533994
-
Mapping of IS6110 insertion sites in Mycobacterium bovis isolates in relation to adaptation from the animal to human host.Vet Microbiol. 2008 Jun 22;129(3-4):333-41. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2007.11.038. Epub 2007 Dec 8. Vet Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18207337
-
Usefulness of spoligotyping To discriminate IS6110 low-copy-number Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex strains cultured in Denmark.J Clin Microbiol. 1999 Aug;37(8):2602-6. doi: 10.1128/JCM.37.8.2602-2606.1999. J Clin Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10405409 Free PMC article.
-
[Molecular epidemiology of Mycobacterium tuberculosis using by RFLP analysis between genomic DNA--its accomplishment and practice].Kekkaku. 2003 Oct;78(10):641-51. Kekkaku. 2003. PMID: 14621573 Review. Japanese.
-
Molecular differentiation of Mycobacterium bovis isolates. Review of main techniques and applications.Res Vet Sci. 2004 Feb;76(1):1-18. doi: 10.1016/s0034-5288(03)00078-x. Res Vet Sci. 2004. PMID: 14659724 Review.
Cited by
-
Droplet digital PCR as alternative to microbiological culture for Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex detection in bovine lymph node tissue samples.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Feb 26;14:1349999. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1349999. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38469351 Free PMC article.
-
Features of Mycobacterium bovis Complete Genomes Belonging to 5 Different Lineages.Microorganisms. 2023 Jan 11;11(1):177. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11010177. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 36677470 Free PMC article.
-
Recent progress in the genotyping of bovine tuberculosis and its rapid diagnosis via nanoparticle-based electrochemical biosensors.RSC Adv. 2023 Oct 30;13(45):31795-31810. doi: 10.1039/d3ra05606f. eCollection 2023 Oct 26. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 37908649 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic Characterization of IS6110 Insertions in Mycobacterium orygis.Evol Bioinform Online. 2024 Apr 4;20:11769343241240558. doi: 10.1177/11769343241240558. eCollection 2024. Evol Bioinform Online. 2024. PMID: 38586439 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allix C., Walravens K., Saegerman C., Godfroid J., Supply P., Fauville-Dufaux M. (2006). Evaluation of the Epidemiological Relevance of Variable-Number Tandem-Repeat Genotyping of Mycobacterium bovis and Comparison of the Method with IS6110 Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism Analysis and Spoligotyping. J. Clin. Microbiol. 44 1951–1962. 10.1128/JCM.01775-05 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benet J.-J., Boschiroli M.-L., Dufour B., Garin-Bastuji B. (2006). Lutte contre la tuberculose bovine en France de 1954 à 2004: Analyse de la pertinence épidémiologique de l’évolution de la réglementation. Epidémiol et santé anim. 1 127–143.
-
- Boschiroli M.-L., Michelet L., Hauer A., De Cruz K., Courcoul A., Hénault S., et al. (2015). Tuberculose bovine en France : cartographie des souches de Mycobacterium bovis entre 2000-2013. Bull. Épidémiol. santé animale alimentation. 70 2–8.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

