Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Action of Cell-Free Culture Extracts and Volatile Organic Compounds Produced by Endophytic Fungi Curvularia Eragrostidis
- PMID: 35814705
- PMCID: PMC9260591
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.920561
Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Action of Cell-Free Culture Extracts and Volatile Organic Compounds Produced by Endophytic Fungi Curvularia Eragrostidis
Abstract
Endophytes are the mutualistic microorganisms that reside within the host plant and promote plant growth in adverse conditions. Plants and their endophytes are engaged in a symbiotic relationship that enables endophytes to access bioactive genes of the ethnomedicinal plants, and, as a result, endophytes are constantly addressed in the sector of pharmaceuticals and agriculture for their multidomain bio-utility. The gradual increase of antimicrobial resistance can be effectively countered by the endophytic metabolites. In these circumstances, in the present investigation, endophytic Curvularia eragrostidis HelS1 was isolated from an ethnomedicinally valuable plant Helecteris isora from East India's forests. The secondary volatile and non-volatile metabolites are extracted from HelS1 and are found to be effective broad-spectrum antimicrobials. A total of 26 secondary metabolites (9 volatiles and 17 non-volatiles) are extracted from the isolate, which exhibits effective antibacterial [against six Gram-positive and seven Gram-negative pathogens with a minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) value ranging from 12.5 to 400 μg ml-1] and antifungal (against seven fungal plant pathogens) activity. The secondary metabolite production was optimised by one variable at a time technique coupled with the response surface methodology. The results revealed that there was a 34% increase in antibacterial activity in parameters with 6.87 g L-1 of fructose (as a carbon source), 3.79 g L-1 of peptone (as a nitrogen source), pH 6.75, and an inoculation period of 191.5 h for fermentation. The volatile metabolite production was also found to be optimum when the medium was supplemented with yeast extract and urea (0.2 g L-1) along with dextrose (40 g L-1). Amongst extracted volatile metabolites, 1-H-indene 1 methanol acetate, tetroquinone, N, N-diphenyl-2-nitro-thio benzamide, Trans 1, 2-diethyl-trans-2-decalinol, naphthalene, and azulene are found to be the most effective. Our investigation opens up opportunities in the sector of sustainable agriculture as well as the discovery of novel antimicrobials against dreadful phyto and human pathogens.
Keywords: broad-spectrum antimicrobial; endophyte; fungi; sustainable agriculture; volatile metabolite.
Copyright © 2022 Santra and Banerjee.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
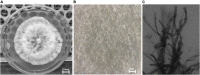


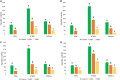
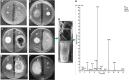

References
-
- Agrios G. N. (2005). Plant Pathology. Amsterdam: Elsevier Academic Press.
-
- Banerjee D., Strobel G. A., Booth B., Sears J., Spakowicz D., Busse S. (2010b). An endophytic Myrothecium inundatum producing volatile organic compounds. Mycosphere 1 241–247.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

