A Multicenter Real-World Study Evaluating the Hepatoprotective Effect of Polyene Phosphatidylcholine Against Chronic Hepatitis B
- PMID: 35814776
- PMCID: PMC9256938
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.842098
A Multicenter Real-World Study Evaluating the Hepatoprotective Effect of Polyene Phosphatidylcholine Against Chronic Hepatitis B
Abstract
Background: Polyene phosphatidylcholine (PPC) has been widely used to treat liver diseases in China. However, there is a lack of post-marketing evidence demonstrating its liver-protective efficiency among patients infected with hepatitis B virus (HBV). This study analyzed the multicenter real-world data to compare the effectiveness of PPC with those of magnesium isoglycyrrhizinate (IsoMag) and glutathione (GSH) in patients with liver injury.
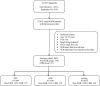
Methods: This study comprised the real-world data analysis of a multicenter, retrospective observational cohort. The data were retrieved from the Cooperative Registry of the Hospital Prescription in China between 1 October 2018, and 30 September 2019. A growth curve analysis was performed to compare the effects of different treatments on liver function longitudinally for up to 30 days after treatment commencement. In addition, the dose effect of the PPC treatment was investigated.
Results: The final cohort included 6,052 patients with approximately 8% infected with HBV (N = 471). There were 1,649, 1,750, and 2,653 patients in the PPC, GSH, and IsoMag groups, respectively, with an average age of 53.9 years. In patients with HBV infection, the PPC treatment was associated with a significant decline in alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) levels (slopes: -3.7, 95% CI, -6.0 to -1.5 U/L/day; -2.4, 95% CI, -4.5 to -0.3 U/L/day, respectively). However, there were no significant differences in the effects among the three groups. In patients without HBV infection, the PPC treatment decreased ALT, AST, γ-glutamyl transferase (GGT), and albumin levels (-5.2, 95% CI, -5.8 to -4.5 U/L/day; -3.5, 95% CI, -4.2 to -2.7 U/L/day; -4.9, 95% CI, -6.2 to -3.7 U/L/day, -0.07, 95% CI, -0.09 to -0.04 g/L/day, respectively) and showed a stronger effect on lowering ALT levels than GSH (-2.6, 95% CI, -3.3 to -1.8 U/L/day, p < 0.05), as well as a stronger effect on lowering GGT levels than IsoMag (-1.4, 95% CI, -2.4 to -0.4 U/L/day, p < 0.05). PPC had no impact on prothrombin activity levels in patients with or without HBV infection. High-dose PPC exhibited a stronger effect on lowering ALT and AST levels than low-dose PPC.
Conclusion: This was the first real-world multicenter study to demonstrate that PPC efficiently lowers ALT and AST levels in patients with liver diseases regardless of the status of HBV infection. PPC treatment showed a comparable or better effect compared with GSH and IsoMag treatments. High-dose PPC resulted in a stronger effect than low-dose PPC.
Keywords: alanine aminotransferase (ALT); aspartate aminotransferase (AST); chronic hepatitis B (CHB); glutathione (GSH); hepatitis B virus (HBV); magnesium isoglycyrrhizinate (IsoMag); polyene phosphatidylcholine (PPC); real world data (RWD).
Copyright © 2022 Xu, Fan, Yu, Han, Kang, Tan, Yang, Chen, Pan and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of polyene phosphatidylcholine and its combination with other drugs in patients with liver diseases based on real-world research.Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2022 Nov;15(11):1363-1375. doi: 10.1080/17512433.2022.2121700. Epub 2022 Sep 11. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36062967
-
Effectiveness and Economic Evaluation of Polyene Phosphatidyl Choline in Patients With Liver Diseases Based on Real-World Research.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Mar 7;13:806787. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.806787. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35330831 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of phosphatidylcholine as adjunctive therapy in improving liver function tests in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and metabolic comorbidities: real-life observational study from Russia.BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2020 Mar 26;7(1):e000368. doi: 10.1136/bmjgast-2019-000368. eCollection 2020. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32337059 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of chronic hepatitis B: case selection and duration of therapy.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002 Apr;17(4):409-14. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1746.2002.02767.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002. PMID: 11982721 Review.
-
INASL Position Statements on Prevention, Diagnosis and Management of Hepatitis B Virus Infection in India: The Andaman Statements.J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2018 Mar;8(1):58-80. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2017.12.001. Epub 2017 Dec 16. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 29743798 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bletilla striata polysaccharides alleviate metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease through enhancing hepatocyte RelA/ HNF1α signaling.World J Gastroenterol. 2025 Jan 28;31(4):93179. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i4.93179. World J Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 39877717 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatoprotective agents in the management of intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy: current knowledge and prospects.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Aug 31;14:1218432. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1218432. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37719856 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases and Chinese Society of Hepatology CMA. The guideline of prevention and treatment for chronic hepatitis B(2019 version). Chin J Clin Infect Dis. (2019) 12:28. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

