The lung ultrasound "Rule of 7" in the prognosis of COVID-19 patients: Results from a prospective multicentric study
- PMID: 35814790
- PMCID: PMC9254652
- DOI: 10.1016/j.medcle.2021.07.024
The lung ultrasound "Rule of 7" in the prognosis of COVID-19 patients: Results from a prospective multicentric study
Abstract
Purpose: There is growing evidence regarding the imaging findings of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in lung ultrasound (LUS), however the use of a combined prognostic and triage tool has yet to be explored.To determine the impact of the LUS in the prediction of the mortality of patients with highly suspected or confirmed COVID-19.The secondary outcome was to calculate a score with LUS findings with other variables to predict hospital admission and emergency department (ED) discharge.
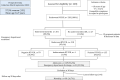
Material and methods: Prospective study performed in the ED of three academic hospitals. Patients with highly suspected or confirmed COVID-19 underwent a LUS examination and laboratory tests.
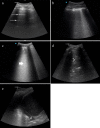
Results: A total of 228 patients were enrolled between March and September 2020. The mean age was 61.9 years (Standard Deviation - SD 21.1). The most common findings in LUS was a right posteroinferior isolated irregular pleural line (53.9%, 123 patients). A logistic regression model was calculated, including age over 70 years, C-reactive protein (CRP) over 70 mg/L and a lung score over 7 to predict mortality, hospital admission and discharge from the ED. We obtained a predictive model with a sensitivity of 56.8% and a specificity of 87.6%, with an AUC of 0.813 [p < 0.001].
Conclusions: The combination of LUS, clinical and laboratory findings in this easy to apply "rule of 7" showed excellent performance to predict hospital admission and mortality.
Objetivo: Existe una evidencia creciente con respecto a los hallazgos de imagen de la enfermedad por coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) en la ecografía pulmonar (LUS), sin embargo, aún no se ha explorado el uso de una herramienta combinada de pronóstico y triaje.El objetivo principal de este estudio fue determinar el impacto de la LUS en la predicción de la mortalidad de los pacientes con sospecha de afectación pulmonar por COVID-19. El objetivo secundario fue calcular una puntuación con los hallazgos del LUS con otras variables para predecir el ingreso hospitalario y el alta del servicio de urgencias (SU).
Material y métodos: Estudio prospectivo realizado en urgencias de tres hospitales académicos, en pacientes con sospecha de COVID-19 o confirmación de esta, a los que se sometió a un examen de LUS y pruebas de laboratorio.
Resultados: Se inscribieron un total de 228 pacientes entre marzo y septiembre de 2020. La edad media fue de 61,9 años (DE 21,1). El hallazgo más común en la LUS fue la irregularidad pleural posteroinferior derecha (53,9%, 123 pacientes). Se calculó un modelo de regresión logística, que incluyó la edad mayor de 70 años, proteína C reactiva (PCR) mayor de 70 mg/L y puntuación de afectación pulmonar mediante LUS score superior a 7 para predecir la mortalidad, el ingreso hospitalario y el alta del SU. Se obtuvo una sensibilidad del 56,8% y una especificidad del 87,6%, con un AUC de 0,813 [p < 0,001] para dicho modelo predictivo, en materia de mortalidad.
Conclusiones: La combinación de LUS, hallazgos clínicos y de laboratorio en esta «regla de 7» de fácil aplicación se mostró de utilidad para predecir el ingreso hospitalario y la mortalidad.
Keywords: C-reactive protein; COVID-19; Chest; Emergency departments; Logistic regression; Point-of-care.
© 2021 Elsevier España, S.L.U. All rights reserved.
Figures
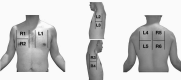
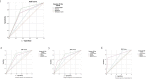
Similar articles
-
The lung ultrasound "Rule of 7" in the prognosis of COVID-19 patients: Results from a prospective multicentric study.Med Clin (Barc). 2022 Jul 8;159(1):19-26. doi: 10.1016/j.medcli.2021.07.012. Epub 2021 Sep 4. Med Clin (Barc). 2022. PMID: 34657744 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing COVID-19 pneumonia-Clinical extension and risk with point-of-care ultrasound: A multicenter, prospective, observational study.J Am Coll Emerg Physicians Open. 2021 May 1;2(3):e12429. doi: 10.1002/emp2.12429. eCollection 2021 Jun. J Am Coll Emerg Physicians Open. 2021. PMID: 33969350 Free PMC article.
-
Point-of-care Lung Ultrasound, Lung CT and NEWS to Predict Adverse Outcomes and Mortality in COVID-19 Associated Pneumonia.J Intensive Care Med. 2022 Dec;37(12):1614-1624. doi: 10.1177/08850666221111731. Epub 2022 Nov 1. J Intensive Care Med. 2022. PMID: 36317355 Free PMC article.
-
Lung ultrasound score predicts outcomes in COVID-19 patients admitted to the emergency department.Ann Intensive Care. 2021 Jan 11;11(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s13613-020-00799-w. Ann Intensive Care. 2021. PMID: 33427998 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between Chest Computed Tomography and Lung Ultrasonography in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19).Ultrasound Med Biol. 2020 Nov;46(11):2918-2926. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2020.07.003. Epub 2020 Jul 13. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32771222 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO. Coronavirus disease pandemic. Im internet: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019 [accessed 09.07.2021].
-
- WHO. Weekly epidemiological update on Coronavirus disease. 5 October 2020. Im Internet: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update---... [accessed 28.10.20].
-
- CDC. Older Adults. 2020. Im Internet: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/need-extra-precautions/older-a... [accessed 25.10.20].
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
