Patient Survival With and Without Radiation Therapy for Early-Stage Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma in the Era of PET and Rituximab
- PMID: 35814857
- PMCID: PMC9260098
- DOI: 10.1016/j.adro.2022.100930
Patient Survival With and Without Radiation Therapy for Early-Stage Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma in the Era of PET and Rituximab
Abstract
Purpose: The benefit of radiation therapy (RT) becomes uncertain in the treatment of early stage diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) in the era of rituximab, positron emission topography (PET), and computed tomography (CT). We sought to retrospectively review modern patients with early stage I-II DLBCL treated with rituximab and staged by PET-CT to better define which patients benefit from consolidative RT.
Methods and materials: Patients with early stage I-II DLBCL from 1998 to 2017 were reviewed coinciding with our institutional utilization of rituximab with the standard regimen of cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone and PET-CT. Relevant clinical information was used to calculate National Comprehensive Cancer Network international prognostic index (IPI) scores. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis and a Cox proportional hazards model were used for overall survival (OS).
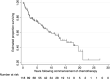
Results: Seventy-seven patients received chemoimmunotherapy alone, and 41 received chemoimmunotherapy plus RT. Median follow-up time was 9.5 years. On univariate analysis, extranodal disease (P = .04) and National Comprehensive Cancer Network IPI (P < .001) were significantly correlated with OS. Five-year OS was 87% versus 67%, and 10-year OS was 67% versus 58%, numerically higher favoring RT (P = .16). On multivariate Cox regression analysis of OS controlling for IPI and extranodal disease, the addition of RT was associated with improved OS (hazard ratio of 0.4, P = .01).
Conclusions: The current analysis supports the use of consolidative RT in early stage DLBCL given an OS benefit on multivariate analysis. Further prospective randomized data are needed to confirm these findings.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Benefit of consolidative radiation in patients with extranodal limited-stage diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a multicenter retrospective study in China.Ann Hematol. 2024 Oct;103(10):4231-4237. doi: 10.1007/s00277-024-05855-0. Epub 2024 Jun 26. Ann Hematol. 2024. PMID: 38922341
-
Benefit of consolidative radiation therapy for primary bone diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2015 May 1;92(1):122-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2015.01.014. Epub 2015 Mar 5. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2015. PMID: 25754633
-
Clinical prognostic factors of diffuse large B cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma: a retrospective study.J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2011 Mar;23(1):17-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jnci.2011.07.003. Epub 2011 Sep 8. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2011. PMID: 22099932
-
Consolidative Radiotherapy after Complete Remission following R-CHOP Immunochemotherapy in Stage III-IV Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Aug 2;15(15):3940. doi: 10.3390/cancers15153940. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37568756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The new German evidence-based guideline on diffuse large B-cell lymphoma-key aspects for radiation oncologists.Strahlenther Onkol. 2023 Feb;199(2):115-120. doi: 10.1007/s00066-022-02035-9. Epub 2023 Jan 4. Strahlenther Onkol. 2023. PMID: 36598520 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Rare Presentation of Collision Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma and Hodgkin Lymphoma Treated with R-CHOP and Adjuvant Radiation Therapy.Cureus. 2024 Jan 20;16(1):e52630. doi: 10.7759/cureus.52630. eCollection 2024 Jan. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38374831 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Horning SJ, Weller E, Kim K, et al. Chemotherapy with or without radiotherapy in limited-stage diffuse aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group study 1484. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:3032–3038. - PubMed
-
- Bonnet C, Fillet G, Mounier N, et al. CHOP alone compared with CHOP plus radiotherapy for localized aggressive lymphoma in elderly patients: A study by the Groupe d'Etude des Lymphomes de l'Adulte. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:787–792. - PubMed
-
- Vargo JA, Gill BS, Balasubramani GK, Beriwal S. Treatment selection and survival outcomes in early-stage diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Do we still need consolidative radiotherapy? J Clin Oncol. 2015;33:3710–3717. - PubMed
-
- Pfreundschuh M, Murawski N, Ziepert M, et al. Radiotherapy (RT) to bulky (B) and extralymphatic (E) disease in combination with 6xR-CHOP-14 or R-CHOP-21 in young good-prognosis DLBCL patients: Results of the 2x2 randomized UNFOLDER trial of the DSHNHL/GLA. J Clin Orthod. 2018;36:7574.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources