Long-term outcome of pathologic myopic foveoschisis treated with posterior scleral reinforcement followed by vitrectomy
- PMID: 35814900
- PMCID: PMC9203488
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2022.06.16
Long-term outcome of pathologic myopic foveoschisis treated with posterior scleral reinforcement followed by vitrectomy
Abstract
Aim: To report the long-term outcome of posterior scleral reinforcement (PSR) followed by vitrectomy for pathologic myopic foveoschisis (MF).
Methods: The records of 27 patients (44 eyes) treated with posterior scleral reinforcement (PSR) followed by vitrectomy for pathologic MF were retrospectively reviewed. The best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA), refractive error, axial length, and spectral-domain optical coherence tomography findings and complications were analyzed.
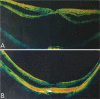
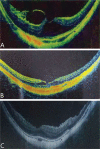
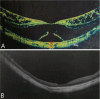
Results: Forty-four eyes of 27 patients were included in this study. The follow-up period was 47.98±18.23mo (24-83mo). The mean preoperative BCVA (logMAR) was 1.13±0.63, and the mean postoperative BCVA was 0.30±0.33 at the last visit. There showed a significant improvement in BCVA postoperatively (P<0.001). Postoperative BCVA in 41 eyes (93%) was improved compared with the preoperative one. Forty-two eyes (95.45%) got total resolution of the MF after surgery. The remaining two eyes (4.55%) got partial resolution of foveoschisis. The preoperative foveal thickness was 610.45±217.11 µm and the postoperative foveal thickness at the last visit was significantly reduced to 177.64±55.40 µm (P<0.001). The preoperative axial length was 29.60±1.71 mm, and the postoperative axial length was 29.74±1.81 mm at the last visit. There was no significant increase in axial length within 47.98±18.23mo of follow-up (P=0.562). There was no recurrence of foveoschisis or occurrence of full-thickness macular hole during the whole follow-up period.
Conclusion: For pathologic MF, PSR followed by vitrectomy is an effective procedure to improve the visual acuity and the anatomical structure of macula. It can also stabilize the axial length for a long time.
Keywords: myopic foveoschisis; posterior scleral reinforcement; vitrectomy.
International Journal of Ophthalmology Press.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Posterior scleral reinforcement combined with vitrectomy for myopic foveoschisis.Int J Ophthalmol. 2016 Feb 18;9(2):258-61. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2016.02.14. eCollection 2016. Int J Ophthalmol. 2016. PMID: 26949646 Free PMC article.
-
Posterior scleral reinforcement and vitrectomy for myopic foveoschisis in extreme myopia.Retina. 2015 Feb;35(2):351-7. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0000000000000313. Retina. 2015. PMID: 25111687
-
Long-term follow-up of vitrectomy in patients with pathologic myopic foveoschisis.Int J Ophthalmol. 2017 Feb 18;10(2):277-284. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2017.02.16. eCollection 2017. Int J Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 28251089 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness and safety of posterior scleral reinforcement with vitrectomy for myopic foveoschisis treatment: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2020 Feb;258(2):257-271. doi: 10.1007/s00417-019-04550-5. Epub 2019 Dec 10. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 31823060
-
Anatomical and visual outcomes in high myopic macular hole (HM-MH) without retinal detachment: a review.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2014 Feb;252(2):191-9. doi: 10.1007/s00417-013-2555-5. Epub 2014 Jan 3. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2014. PMID: 24384802 Review.
Cited by
-
Internal limiting membrane peeling combined with silicone oil or air tamponade for highly myopic foveoschisis.Int J Ophthalmol. 2024 Jun 18;17(6):1079-1085. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2024.06.13. eCollection 2024. Int J Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 38895672 Free PMC article.
-
Visualized analysis of research on myopic traction maculopathy based on CiteSpace.Int J Ophthalmol. 2023 Dec 18;16(12):2117-2124. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2023.12.26. eCollection 2023. Int J Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 38111942 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Duan TQ, Tan W, Yang J, Li FL, Xiong SQ, Wang XG, Xu HZ. Morphological characteristics predict postoperative outcomes after vitrectomy in myopic traction maculopathy patients. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging Retina. 2020;51(10):574–582. - PubMed
-
- Wang LF, Wang YH, Li YL, Yan ZY, Li YH, Lu L, Lu TX, Wang X, Zhang SJ, Shang YX. Comparison of effectiveness between complete internal limiting membrane peeling and internal limiting membrane peeling with preservation of the central fovea in combination with 25G vitrectomy for the treatment of high myopic foveoschisis. Medicine. 2019;98(9):e14710. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Iwasaki M, Miyamoto H, Okushiba U, Imaizumi H. Fovea-sparing internal limiting membrane peeling versus complete internal limiting membrane peeling for myopic traction maculopathy. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2020;64(1):13–21. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
