Radiomics in prostate cancer: an up-to-date review
- PMID: 35814914
- PMCID: PMC9260602
- DOI: 10.1177/17562872221109020
Radiomics in prostate cancer: an up-to-date review
Abstract
Prostate cancer (PCa) is the most common worldwide diagnosed malignancy in male population. The diagnosis, the identification of aggressive disease, and the post-treatment follow-up needs a more comprehensive and holistic approach. Radiomics is the extraction and interpretation of images phenotypes in a quantitative manner. Radiomics may give an advantage through advancements in imaging modalities and through the potential power of artificial intelligence techniques by translating those features into clinical outcome prediction. This article gives an overview on the current evidence of methodology and reviews the available literature on radiomics in PCa patients, highlighting its potential for personalized treatment and future applications.
Keywords: MRI; PET-CT; artificial intelligence; prostate cancer; radiomics.
© The Author(s), 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
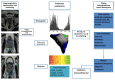
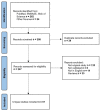
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al.. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2018; 68: 394–424. - PubMed
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al.. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2021; 71: 209–249. - PubMed
-
- Maggi M, Gentilucci A, Salciccia S, et al.. Psychological impact of different primary treatments for prostate cancer: a critical analysis. Andrologia 2019; 51: e13157. - PubMed

