Comparative Potential of Zinc Sulfate, L-Carnitine, Lycopene, and Coenzyme Q10 on Cadmium-Induced Male Infertility
- PMID: 35814917
- PMCID: PMC9262569
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/6266613
Comparative Potential of Zinc Sulfate, L-Carnitine, Lycopene, and Coenzyme Q10 on Cadmium-Induced Male Infertility
Abstract
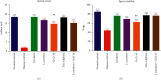
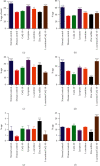
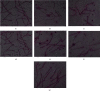
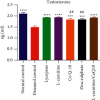
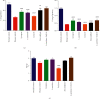
The human exposure to toxic chemicals and heavy metals is one of the main predisposing factors contributing to male infertility. Acute exposure to cadmium chloride results in testicular damage and infertility. The purpose of the present study was to investigate and compare the curative effect of coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10), lycopene, L-carnitine (LC), and zinc sulfate against the cadmium-induced infertility in male Wistar rats. Cadmium chloride (0.4 mg/kg/day) was orally administered to rats for three consecutive days. Then, oral administration of different treatments (i.e., LC 100 mg/kg, CoQ10 20 mg/kg, lycopene 4 mg/kg, zinc sulfate 6 mg/kg, and a combination LC-CoQ10 at 500/50 mg/kg) was carried out for 30 days. The impact of different treatments on semen parameters, such as sperm count and motility, testicular antioxidants, and serum testosterone, was determined. Furthermore, the morphology of epididymis sperms and histopathology of rat testes were also assessed. Cadmium exposure decreased the sperm count, progressive sperm motility, testosterone, superoxide dismutase (SOD), and catalase and reduced glutathione (GSH). It also caused banana sperm tail, bent sperm head, vacuolization of seminiferous tubules, and oligospermia in rat testes. All treatments with nutraceuticals improved sperm count, sperm morphology, serum testosterone, vacuolization of seminiferous tubules, and oligospermia in diseased rats. Treatment with lycopene, LC, and LC-CoQ10 improved progressive sperm motility and other parameters and increased SOD, GSH, and CAT in the rat testes. CoQ10 also increased SOD activity in rat testes' tissue homogenates. It is concluded from the current study that all nutraceuticals partially improved reproductive toxicity of cadmium. The administration of lycopene and a high-dose combination of LC-CoQ10 were more efficacious in treating cadmium-induced infertility than other treatments. Treatment of cadmium-exposed rats with lycopene, LC, CoQ10, and LC-CoQ10 improved sperm count and motility through reduction of testicular oxidative stress and improving serum testosterone.
Copyright © 2022 Ayesha Iftikhar et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Testicular toxicity and sperm quality following copper exposure in Wistar albino rats: ameliorative potentials of L-carnitine.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018 Jan;25(2):1837-1862. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-0624-8. Epub 2017 Nov 4. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29103113
-
Selenium and lycopene attenuate cisplatin-induced testicular toxicity associated with oxidative stress in Wistar rats.Urology. 2012 May;79(5):1184.e1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2011.12.006. Urology. 2012. PMID: 22546410
-
Does coenzyme Q10 improve semen quality and circulating testosterone level? a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 3;15:1497930. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1497930. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39830337 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Coenzyme Q10 and Selenium on Seminal Fluid Parameters and Antioxidant Status in Men with Idiopathic Infertility.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2021 Apr;199(4):1246-1252. doi: 10.1007/s12011-020-02251-3. Epub 2020 Jun 22. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2021. PMID: 32572802 Clinical Trial.
-
Antioxidant supplements and semen parameters: An evidence based review.Int J Reprod Biomed. 2016 Dec;14(12):729-736. Int J Reprod Biomed. 2016. PMID: 28066832 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Does coenzyme Q10 supplementation protect spermatogenesis in ciprofloxacin-induced rat testes?Clin Exp Reprod Med. 2025 Jun;52(2):167-177. doi: 10.5653/cerm.2024.07017. Epub 2024 Sep 20. Clin Exp Reprod Med. 2025. PMID: 39301757 Free PMC article.
-
Coenzyme Q10 and Xenobiotic Metabolism: An Overview.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 17;26(12):5788. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125788. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40565253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early Zinc Supplementation Enhances Epididymal Sperm Glycosylation, Endocrine Activity, and Antioxidant Activity in Rats Exposed to Cadmium.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 10;26(10):4589. doi: 10.3390/ijms26104589. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40429736 Free PMC article.
-
Heavy Metal Exposure: Molecular Pathways, Clinical Implications, and Protective Strategies.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Jan 5;13(1):76. doi: 10.3390/antiox13010076. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38247500 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abu-Naser S. S. Male infertility expert system diagnoses and treatment. American Journal of Innovative Research and Applied Sciences . 2016;7:1–12.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

