Inhibition of MARK4 by serotonin as an attractive therapeutic approach to combat Alzheimer's disease and neuroinflammation
- PMID: 35814926
- PMCID: PMC9215163
- DOI: 10.1039/d2md00053a
Inhibition of MARK4 by serotonin as an attractive therapeutic approach to combat Alzheimer's disease and neuroinflammation
Abstract
Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) govern various cellular programs and crucial intermediate pathways in signaling. Microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 4 (MARK4) is a part of the kinase family recognized for actively phosphorylating neural microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs) like MAP2, MAP4 and most importantly, tau. The Ser/Thr kinase MARK4 overexpression is associated with various life-threatening conditions such as neurodegenerative disorders, diabetic neuropathy, and cancer. Functionally, MARK4 is correlated with many important signaling cascades and transcription factors contributing to neurodegeneration and cancer onset and progression. Serotonin is a key molecule associated with regulating mood, stress, and various behavioral aspects. Low serotonin levels promote the progression of neurological and psychotic disorders, which is also a consequence of tau accumulation. MARK4 being a major contributor to phosphorylating tau, leading to its accumulation, and contributing to tauopathy, is targeted for inhibition by serotonin. The study deals with the inhibition of MARK4 by serotonin using combined computational and experimental studies. The results presented in this paper provide strong evidence for the direct physical binding of serotonin to recombinant MARK4 and subsequent inhibition of its kinase activity. In addition, we have performed molecular docking, followed by 100 ns MD simulations of MARK4 in the presence of serotonin, to estimate the stability of the protein-ligand complex. Since MARK4 is a potential drug target and can be exploited for drug design and discovery for cancer and neurodegenerative disorders, the results presented here are of interest and may be further exploited for Alzheimer's disease (AD) and other neurodegenerative diseases.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
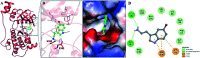
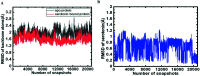

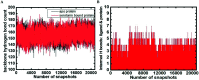
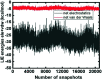

Similar articles
-
Inhibition of Microtubule Affinity Regulating Kinase 4 by Metformin: Exploring the Neuroprotective Potential of Antidiabetic Drug through Spectroscopic and Computational Approaches.Molecules. 2022 Jul 21;27(14):4652. doi: 10.3390/molecules27144652. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35889524 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting inhibition of microtubule affinity regulating kinase 4 by Harmaline: Strategy to combat Alzheimer's disease.Int J Biol Macromol. 2023 Jan 1;224:188-195. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.10.115. Epub 2022 Oct 17. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023. PMID: 36257368
-
Mechanistic insights into MARK4 inhibition by galantamine toward therapeutic targeting of Alzheimer's disease.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Sep 19;14:1276179. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1276179. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37795023 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic targeting of microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 4 in cancer and neurodegenerative diseases.J Cell Biochem. 2023 Sep;124(9):1223-1240. doi: 10.1002/jcb.30468. Epub 2023 Sep 3. J Cell Biochem. 2023. PMID: 37661636 Review.
-
Microtubule-affinity regulating kinase 4: A potential drug target for cancer therapy.Cell Signal. 2022 Nov;99:110434. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2022.110434. Epub 2022 Aug 9. Cell Signal. 2022. PMID: 35961526 Review.
Cited by
-
In silico investigations identified Butyl Xanalterate to competently target CK2α (CSNK2A1) for therapy of chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Sci Rep. 2022 Oct 21;12(1):17648. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-21546-0. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36271116 Free PMC article.
-
Apigenin-mediated MARK4 inhibition: a novel approach in advancing Alzheimer's disease therapeutics.Mol Divers. 2025 Jan 22. doi: 10.1007/s11030-025-11104-x. Online ahead of print. Mol Divers. 2025. PMID: 39841316
-
Unraveling human transferrin-tryptamine interactions: a computational and biophysical approach to Alzheimer's disease therapeutics.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 19;16:1540736. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1540736. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40176911 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular landscape of the overlap between Alzheimer's disease and somatic insulin-related diseases.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2024 Oct 28;16(1):239. doi: 10.1186/s13195-024-01609-2. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 39465382 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Microtubule Affinity Regulating Kinase 4 by Metformin: Exploring the Neuroprotective Potential of Antidiabetic Drug through Spectroscopic and Computational Approaches.Molecules. 2022 Jul 21;27(14):4652. doi: 10.3390/molecules27144652. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35889524 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Chemical Information
Miscellaneous

